What Are 2 Facts About The Solar System?
The Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of our solar system and is responsible for the Earth’s climate and weather. The Sun is an average-sized yellow dwarf star and contains 99.86% of the mass of the entire solar system (https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/factfile-the-sun.html). It formed over 4.5 billion years ago and is composed of hydrogen and helium. The Sun’s outer visible layer is called the photosphere which has a temperature of 5,800K (https://science.nasa.gov/sun/facts/).
Planets
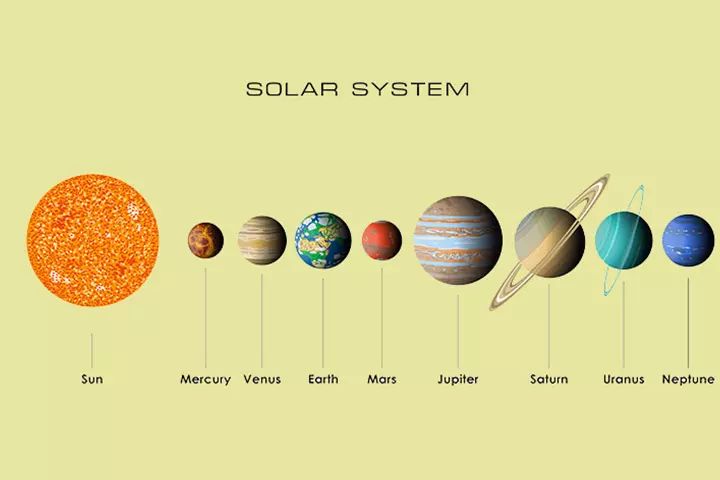
There are eight planets in our solar system. The planets, in order from the Sun, are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune (NASA).
The four planets closest to the Sun – Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars – are called the terrestrial planets. They have solid, rocky surfaces. The four large planets farther from the Sun – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune – are called the gas giants. They do not have solid surfaces, but are made up of gases like hydrogen and helium.
Earth is the only planet known to have liquid water on its surface. Earth’s atmosphere protects the planet from asteroid impacts and solar radiation. Earth is the only planet known to support life (Sky & Telescope).
Mars has ice caps that grow and recede with the seasons. Mars may have once supported life. NASA spacecraft are currently exploring Mars and searching for signs of ancient life.
Jupiter is made up of swirling clouds and is the largest planet in our solar system. Jupiter has a giant red spot that is actually a huge storm bigger than Earth. Jupiter has over 60 moons.
Saturn has over 150 moons. Saturn has beautiful rings made up of ice and rock particles. Saturn’s largest moon Titan has lakes of liquid methane.
Uranus rotates on its side and is an ice giant. The methane atmosphere gives Uranus its blue green color. Uranus has faint rings and over 20 moons.
Neptune is dark, cold, and very windy. Neptune has a rocky core surrounded by ice, liquid, and gas. Neptune has 14 known moons.
Dwarf Planets
Pluto is the largest dwarf planet in our solar system with a diameter of approximately 1,477 miles. It has 5 moons: Charon, Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra. Pluto orbits the sun on average 3.7 billion miles away. In 2006, Pluto was demoted from planet status to dwarf planet status by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). This was because Pluto failed to meet all the criteria needed to be classified as a full-sized planet. Specifically, Pluto had not cleared its neighboring region of other objects. The IAU currently recognizes 5 dwarf planets: Ceres, Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, and Eris. They orbit the sun just like other planets, but are smaller and have not cleared their orbital paths (source).
Ceres is the only dwarf planet located in the inner solar system. It orbits in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. With a diameter of 587 miles, it is the smallest dwarf planet but is still the largest object in the asteroid belt. Ceres is composed of rock and ice and may have an ocean of liquid water under its crust (source).
Haumea and Makemake are icy dwarf planets that orbit beyond Neptune in the Kuiper Belt. Haumea measures about 1,150 miles in diameter and has two moons. It is elongated in shape due to its rapid rotation. Makemake is about 890 miles in diameter and likely has a surface covered in frozen methane (source).
Eris is the most distant dwarf planet, orbiting about 9 billion miles from the Sun on average. With a diameter of 1,445 miles, it is nearly the same size as Pluto. Eris has one known moon called Dysnomia. When Eris was first discovered in 2005, it was thought to be larger than Pluto, so there was a debate over which object should be classified as a planet. This led to Pluto’s demotion and the creation of the dwarf planet category (source).
Asteroid Belt
The asteroid belt is a region of space between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter where most of the asteroids in our solar system are found. Here are some key facts about the asteroid belt:
The asteroid belt contains millions of asteroids, although the total mass is only about 4% the mass of the Moon. The largest asteroid is Ceres at almost 600 miles wide. NASA
The asteroid belt is estimated to be approximately 140 million miles across and lies between 2.2 and 3.2 astronomical units from the Sun. One astronomical unit (AU) is the distance between the Earth and Sun, about 93 million miles. ThePlanets.org
Despite containing millions of asteroids, they are spread out very far apart. A spacecraft could easily pass through the asteroid belt without hitting an asteroid. The gravity of Jupiter beyond the belt acts to keep the asteroids more widely dispersed. Space.com
The asteroid belt likely represents the remnants of the primordial solar nebula disk that never formed into planets. Collisions over billions of years have broken up most large asteroids. Space.com
Moons
According to NASA, there are over 200 moons in our solar system orbiting the planets and dwarf planets [1]. The planet with the most moons is Jupiter, which has 79 confirmed moons orbiting it [2]. Some interesting facts about moons in our solar system include:
Saturn’s moon Titan has a thick atmosphere and is the only moon in the solar system known to have surface liquids. Titan’s atmosphere is primarily nitrogen and has methane lakes and rivers on its surface [1].
Jupiter’s moon Ganymede is the largest moon in our solar system at 3,273 miles in diameter, making it larger than the planet Mercury [2].
Earth’s moon is the 5th largest moon in the solar system. Its diameter is 2,159 miles, and it is tidally locked to Earth, meaning the same side always faces the Earth [1].
Mars has two small moons called Phobos and Deimos that have irregular shapes and are believed to possibly be captured asteroids [2].
Neptune’s moon Triton orbits the planet in a reverse direction compared to most moons, suggesting it may have been captured by Neptune’s gravity [1].
[1] https://science.nasa.gov/solar-system/moons/
[2] https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/how-many-moons/
Rings
Some planets in our solar system have beautiful rings surrounding them. The most well-known rings belong to the planet Saturn. Saturn’s rings are made up of chunks of ice and rock that orbit the planet. According to NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, Saturn’s rings can be up to 30 feet thick and are composed of billions of particles ranging in size from tiny grains to giant boulders (NASA). The rings orbit Saturn above its equator and can extend up to 175,000 miles from the planet.
Saturn isn’t the only planet with rings though. Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune also have their own ring systems. The rings are believed to be debris left over from comets, asteroids, or shattered moons (Webb). The particles in the rings orbit the planet and can help stabilize or destabilize moons. Rings are an example of how complex our solar system is.
Comets
Comets are icy, small Solar System bodies that orbit the Sun. When close enough to the Sun they display a visible coma (a fuzzy outline or atmosphere due to solar radiation) and sometimes a tail. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust and small rocky particles.
The majority of comets have highly elliptical orbits that take them close to the Sun for a small part of their orbit and bring them very far from the Sun for the remainder. Some comets have an orbit that is completely hyperbolic; that is, they orbit the Sun once and then leave the Solar System forever. The influence of Jupiter’s gravity is thought to fling comets into interstellar space.
Comets leave behind a trail of debris that can lead to meteor showers on Earth. For example, the Perseid meteor shower occurs every year between August 9 and 13 when the Earth passes through the orbit of the Swift-Tuttle Comet.
Meteoroids
Meteoroids are small particles that orbit the sun and range in size from dust grains to small asteroids. According to NASA, meteoroids originate from comets or asteroids https://science.nasa.gov/solar-system/meteors-meteorites/. Meteoroids can be composed of rock, iron, ice, or a combination of these materials. As they travel through space, the trajectories of meteoroids are influenced by the gravity of planets and larger bodies. While floating in space, meteoroids do not produce light and are very difficult to observe directly.
Meteoroids drift through the solar system and can reach speeds over 45,000 mph relative to the Earth. They are concentrated in rings along the orbital paths of their parent comets and asteroids. The asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter contains a large population of meteoroids https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/meteoroid. On occasion, the trajectory of a meteoroid will intersect with a planet or moon, allowing it to enter the atmosphere. At this point, the high-velocity meteoroid vaporizes due to friction and creates a meteor or shooting star visible from the surface below.
Distance
The distances between objects in our solar system are truly vast. As an example, the average distance between the Earth and Sun is about 149 million km or 92 million miles (1 astronomical unit) [1]. To put that into perspective, it takes sunlight over 8 minutes to travel from the Sun to Earth. Meanwhile, the distance between the planets can range dramatically depending on their position in orbit. Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, orbits at a distance of about 58 million km at its closest approach, while Neptune, the farthest planet, orbits at a distance of about 4.5 billion km at its farthest point [2]. This massive scale is difficult to comprehend, but it demonstrates the true expanse of our solar system.
Origins
The solar system formed about 4.5 billion years ago from a giant cloud of gas and dust known as the solar nebula. As the cloud collapsed under its own gravity, the material spun faster and flattened into a disk. At the center, the material became dense and hot, forming the Sun. Farther out, small grains stuck together to form clumps called planetesimals, which collided and combined to create planets. The solar wind swept lighter elements like hydrogen and helium to the outer reaches, while heavier elements like iron and nickel sank to the center to form the Sun and inner planets. The small amounts of remaining debris now orbit as asteroids and comets.
According to NASA, the earliest materials to form in the solar nebula included calcium- and aluminum-rich inclusions up to 4.56 billion years old (NASA). These indicate that the solar system coalesced early in the history of the universe.