Solar Energy Solutions: Meeting The Growing Demand
The demand for solar energy and other renewable clean energy solutions is growing rapidly worldwide. This growth is driven by several converging factors:
– Climate change and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from burning fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. Solar and wind energy produce no direct emissions.
– Concerns about energy security and reliance on imported fossil fuels. Solar and wind utilize abundant domestic energy sources.
– Technological improvements that have dramatically lowered the cost of solar and wind power, making them cost competitive with conventional power sources.
– Supportive government policies such as tax credits, feed-in tariffs, renewable portfolio standards and carbon pricing, which help accelerate the transition to clean energy.
– Corporate and consumer demand for clean energy due to environmental concerns. Companies are buying more clean power and households are installing solar panels.
– The plummeting price of battery storage, enabling solar and wind to provide around-the-clock carbon-free energy.
As the world seeks to address climate change and air pollution while meeting rising energy demand, solar power is poised to play a major role in displacing fossil fuels and building a clean energy economy.
Benefits of Solar
Solar energy offers numerous advantages as a clean, renewable source of power. Unlike fossil fuels, it does not require burning fuel, emit greenhouse gases or generate hazardous waste. After the initial energy investment in manufacturing and installing solar panels, the fuel (sunlight) is free. This makes solar an inexpensive long-term energy solution.
Solar PV systems can operate for decades with little maintenance, producing clean electricity from sunlight. Being powered by the sun, solar energy production aligns with peak daylight hours when electricity demand is highest. Solar PV can be installed almost anywhere with exposure to sunlight, allowing distributed power generation. It can help reduce reliance on centralized fossil fuel power plants and tangled transmission networks vulnerable to outages.
Solar supports energy independence, allowing homeowners and businesses to generate their own power. It increases resiliency against grid disruptions and electricity price hikes. Solar PV scales easily, produces no noise or pollution and has found diverse applications from powering small devices to large utility-scale solar farms. As technology advances and costs decline, solar adoption continues to grow rapidly across the globe.
Challenges and Limitations
While solar power offers many benefits, it also comes with some inherent challenges and limitations that must be addressed for it to reach its full potential.
One of the biggest challenges with solar is intermittency. Since the sun does not shine 24/7, solar output varies throughout the day and year. Solar only generates power when the sun is shining, so it lacks the consistent baseload power of fossil fuels and nuclear. This intermittency makes integrating large amounts of solar more complex for grid operators.
The variability of solar also highlights the need for energy storage solutions. Storing excess solar generation during peak sunlight hours for use at night or during cloudy weather can help overcome intermittency. However, large-scale, cost-effective storage technologies are still under development.
Additionally, solar power is currently more expensive than conventional power sources on a per kilowatt-hour basis. While costs have dropped dramatically in recent decades, additional innovations are needed to increase efficiencies and bring down costs further.
Improving Efficiency
Two key ways to improve the efficiency of solar energy systems are through developing new solar cell materials and advanced tracking systems. Traditional silicon solar cells have a maximum efficiency around 20-25%. New thin-film materials like perovskites and quantum dots offer potential efficiencies above 30% along with lower costs. Research is focused on making these new materials stable enough for long-term use. Dual-sided solar panels that can absorb light from both sides can also boost efficiency.
Solar tracking systems allow panels to follow the sun’s path, maximizing exposure to sunlight throughout the day. Single-axis trackers tilt panels east to west with the sun, while dual-axis trackers also adjust the north-south orientation. Trackers can increase solar panel output by 20-30% compared to fixed tilt systems. Intelligent tracking algorithms and sensors that account for weather and seasons are advancing this technology further. Overall, these improvements in materials and tracking will help solar panels convert a greater portion of sunlight into useful energy.
Storage Solutions
As solar energy generation grows, storage solutions become increasingly important to capture and harness the energy when production exceeds demand. There are several key storage technologies that help address the intermittency of solar power.
Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have become the dominant battery storage solution for solar energy. Compared to lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion offers higher efficiency, lower self-discharge, minimal maintenance, and a longer lifespan. Battery costs have declined significantly in recent years, making them more viable for large-scale energy storage. Advances in battery chemistry and manufacturing are expected to further improve performance and storage capacity.
Pumped Hydro Storage
Pumped hydro accounts for over 90% of utility-scale energy storage worldwide. It involves pumping water uphill to a reservoir when energy supply exceeds demand, then releasing it through hydroelectric turbines when extra energy is needed. Pumped hydro provides a proven long-duration storage solution, but site selection can be constrained by geography and high capital costs.
Thermal Storage
Thermal energy storage allows excess heat to be stored for later use. Molten salt storage is often used in concentrated solar power plants to retain thermal energy and extend power generation after sunset. Chilled water tanks can store cooling capacity generated by solar PV systems to shift load and reduce peak electricity demand. Thermal storage provides a low-cost storage medium to balance energy supply and demand.
Smart Grid Integration
As more solar energy comes online, integrating these distributed energy resources into the electric grid becomes increasingly important. Smart grid technology enables two-way communication between the utility and solar panel owners, allowing for more dynamic and optimized power flows.
Net metering policies credit solar panel owners for the excess power they export to the grid. Forecasting tools help utilities predict the variable solar generation more accurately across different timeframes. These capabilities allow for greater grid flexibility and stability as solar penetration rises.
Investments into modernizing the aging grid infrastructure are crucial. Improved transmission lines, energy storage, and smart inverters will prevent bottlenecks and disruptions as more solar electricity is generated. With the right technologies and policies, the grid can facilitate a smooth transition to a more decentralized and renewable-based system.
Policy and Regulations
Governments around the world are implementing policies and regulations to accelerate the adoption of solar energy. Key policies include:
Tax Credits
Many countries offer tax credits and other financial incentives for installing solar panels or investing in solar companies. These help reduce the upfront costs of going solar. The US has a federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) that allows homeowners to deduct 26% of solar installation costs from their taxes. Similar credits exist in other nations.
Net Metering
Net metering policies allow homes and businesses with solar panels to get credit on their utility bills for excess electricity fed back into the grid. This makes installing solar more financially viable. Over 40 US states have mandatory net metering laws. Countries like India, Japan, and Germany also use net metering.
Renewable Portfolio Standards
Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) require utilities to source a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources. This creates guaranteed demand for solar power. Over 70% of US states have RPS policies, along with the EU, China, and other major markets.
Cost Competitiveness
Solar energy has become increasingly cost-competitive with fossil fuel sources due to rapidly falling prices. The cost of solar panels and installation has dropped dramatically over the past decade. This has enabled solar power to achieve grid parity in many parts of the world, meaning it can generate electricity at a cost equal to or cheaper than the local utility rate.
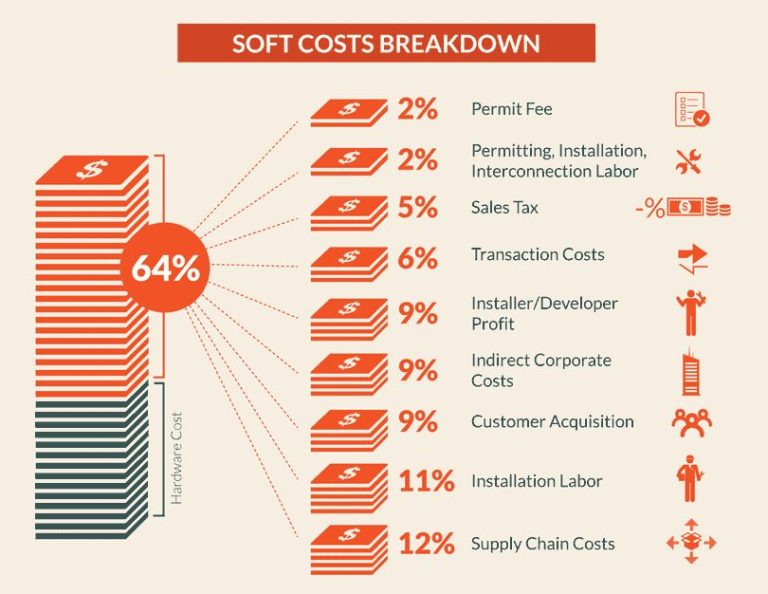
The average price of solar panels has declined around 90% since 2010 as a result of improved manufacturing processes and economies of scale. Additionally, the “soft costs” of installation like permitting, labor, and customer acquisition have fallen as the residential and commercial solar markets have matured.
Solar’s levelized cost of electricity (LCOE), which factors in lifetime system costs, is now on par with coal, nuclear and natural gas in multiple regions globally. According to Lazard’s annual analysis, utility-scale solar PV and onshore wind are the cheapest sources of new electricity generation in many countries, even without subsidies. As the LCOE of solar continues to decrease, it will become increasingly dominant as an affordable, renewable energy source worldwide.
Expanding Applications
As solar technology improves and costs decline, solar is expanding into new applications across the residential, commercial and utility sectors.
Residential
Homeowners are increasingly adopting rooftop solar systems to reduce electricity bills. Solar panels can offset 50-100% of household energy use. With net metering, excess power is exported to the grid. Solar home systems provide clean, renewable power and energy independence. Declining system prices and financing options make residential solar affordable.
Commercial
Businesses are utilizing solar to reduce overhead costs and meet sustainability goals. Roof, parking canopy and ground mount systems generate power for offices, warehouses, retail stores and manufacturing plants. Commercial solar arrays can be sized from 10 kW up to the megawatt scale. Onsite solar helps companies take control of energy expenses, hedge against utility rate increases and boost green branding.
Utility-Scale
Large solar farms owned by utilities are rapidly expanding to meet renewable energy targets. Utility-scale systems are usually ground-mounted, ranging from 1 to over 100 megawatts. These massive solar plants feed electricity directly into the grid. With economies of scale and supportive policies, utility solar costs have fallen below fossil fuels. Massive solar farms will be key for transitioning electric grids to carbon-free generation.
Future Outlook
The future looks very bright for solar energy. Most projections show solar energy production growing exponentially in the coming decades. This growth will be driven by several key factors:
Falling Prices – Solar panel prices have dropped dramatically in the past decade, making solar power cost competitive with fossil fuels. As production scales up further, prices are projected to continue falling. This will enable more widespread adoption globally.
Increased Efficiency – Researchers continue to make advances in solar cell technology, progressively increasing their efficiency in converting sunlight to electricity. More efficient panels mean lower costs and higher energy output.
Supportive Policies – Governments around the world are implementing policies to encourage solar power generation, such as tax credits, renewable energy mandates, and streamlined permitting. These policies will further accelerate the growth.
Global Adoption – Developing nations are expected to drive much of the growth in solar energy. Places like Africa and Southeast Asia, where electricity access is still limited, can leapfrog directly to solar power. The plummeting prices make solar a cost-effective solution.
If current trends continue, most analysts expect solar power to become one of the dominant electricity sources worldwide within the next few decades. The technology holds great promise for providing clean, renewable energy to meet the planet’s growing demand.