Is Renewable Energy Better Than Nuclear Energy
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, geothermal, and hydropower are gaining popularity as clean alternatives to fossil fuels. Nuclear energy, which produces no greenhouse gases, is also promoted as a low-carbon energy source. But is renewable energy truly better for the environment than nuclear power? This article compares the pros and cons of renewable energy and nuclear power.
The thesis of this article is that renewable energy is generally better for the environment than nuclear energy. Renewables like solar and wind energy have minimal environmental impacts once installed and can be deployed more quickly than nuclear power. While nuclear energy produces very low emissions, the risk of accidents and the issue of radioactive waste are key downsides. Overall, renewable energy is cleaner and safer than nuclear.
What is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy is energy that comes from natural sources or processes that are constantly replenished. Some examples of renewable energy sources are solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass. Unlike fossil fuels, which draw on finite resources that may eventually become too expensive or environmentally damaging to retrieve, renewable energy sources are generally unlimited in availability.
Solar energy comes from the solar radiation from the sun, which can be converted into electricity using photovoltaic solar panels or concentrated to generate heat. Wind power utilizes the airflow from wind to turn large wind turbines that power generators. Hydropower harnesses the energy from flowing water, generally from dams, to produce electricity. Geothermal energy taps into the natural heat under the earth’s surface for heating or to generate clean electricity. Biomass utilizes organic plant or animal waste to generate energy.
Because renewable energy comes from naturally recurring sources, it has less environmental impact than burning fossil fuels, which emits greenhouse gases linked to climate change. Development of renewable sources provides energy security as well, since the supply will not be affected by the scarcity of finite fossil fuel resources.
Pros of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy has several advantages over fossil fuels. First and foremost, renewables produce little to no global warming emissions. Unlike coal and natural gas, renewable sources of energy like wind, solar, and hydropower don’t emit greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change. According to the EPA, the use of renewable energy in 2018 avoided 203 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions. Replacing fossil fuels with renewables can significantly lower carbon emissions and help mitigate the effects of global warming.
In addition, renewable energy diversifies energy supply and makes countries more energy independent. Over-reliance on imported fossil fuels can create economic vulnerabilities. In contrast, renewable energy is available domestically in most countries. By harnessing sun, wind, water sources at home, nations can become more energy self-sufficient.
Furthermore, renewable energy results in cleaner air and improved public health. Burning fossil fuels releases pollutants like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and particulate matter that can cause smog, acid rain, and respiratory illnesses. Renewables reduce these air pollutants, improving air quality and preventing asthma attacks, respiratory diseases, and premature deaths linked to pollution.
Cons of Renewable Energy
While renewable energy has many benefits, there are some downsides to consider as well. Two of the main cons are high upfront costs and intermittent power generation.
Most renewable energy technologies require large initial investments to build and install the equipment. For example, constructing a wind or solar farm can cost millions of dollars upfront, even though the fuel itself (wind and sunlight) is free (Energysage, 2022). The costs are often passed on to consumers through their energy bills, making renewable energy more expensive in the short term.
Many renewable sources also provide power intermittently, meaning they only generate electricity when the resource is available. Solar panels don’t work at night, and wind turbines stop spinning when there’s no wind. This can make it challenging to integrate renewables into the existing grid infrastructure without adequate energy storage solutions (Greenmatch, 2022).
What is Nuclear Energy?
Nuclear energy comes from the splitting of uranium atoms in a process called nuclear fission. Uranium atoms are bombarded with neutrons, causing them to split into lighter atoms and release energy in the form of heat. This heat is used to boil water into steam that spins a turbine to generate electricity. The process takes place inside the core of nuclear reactors – specialized facilities that contain and control nuclear chain reactions.
Nuclear power plants operate by utilizing the heat from nuclear fission to produce electricity. The core of the nuclear reactor contains fuel rods made of uranium pellets stacked end-to-end. Control rods are inserted into the core to absorb neutrons and regulate the rate of fission. A moderator – often water – surrounds the fuel rods to slow down the neutrons for a more efficient chain reaction. The enormous amount of heat generated by nuclear fission turns the water into steam, which then drives turbine generators to produce electricity.
Overall, nuclear energy works by releasing energy trapped inside the nucleus of uranium atoms through fission. This process is carefully controlled and contained within nuclear reactors at power plants to safely harness that energy and convert it into usable electricity.
Pros of Nuclear Energy
One of the key advantages of nuclear energy is that it provides reliable, on-demand baseload power that is not dependent on weather conditions. Nuclear power plants have very high capacity factors, meaning they operate at full power over 90% of the time (https://www.energy.gov/ne/articles/advantages-and-challenges-nuclear-energy). This makes nuclear a consistent source of electricity compared to intermittent renewables like wind and solar. Nuclear plants continuously produce large amounts of carbon-free energy, operating as a stable grid asset (https://www.edfenergy.com/energywise/what-are-advantages-nuclear-energy). Having nuclear as part of a diverse energy mix helps ensure a steady supply of electricity to meet base demand.
Cons of Nuclear Energy
There are several notable cons to consider with nuclear energy:
There is Risk of Accidents. Nuclear energy has the possibility of extremely detrimental impacts in the unlikely event of an accident or radioactive material release. Some major nuclear accidents like Chernobyl and Fukushima have shown that the consequences of a mishap at a nuclear power plant can be severe.
Radioactive Waste is another significant disadvantage of nuclear power. The radioactive waste produced during nuclear fission remains dangerous for many thousands of years. There is still an unresolved question of how to dispose of nuclear waste safely in the long-term. Currently waste is stored on-site at plants, but there are concerns about the risks if storage containers fail over time. The safe storage of nuclear waste is a major challenge.
Comparing Environmental Impacts
When examining the environmental impacts of nuclear energy versus renewable energy, there are a few key factors to consider:
Carbon emissions – Nuclear energy produces very low carbon emissions over its lifecycle, comparable to renewable sources like wind and solar. According to Our World in Data, nuclear results in 30 times fewer carbon emissions than gas and 45 times fewer than coal per unit of electricity generated (Ritchie, 2023). Renewables like wind and solar have no direct carbon emissions, giving them an advantage over nuclear.
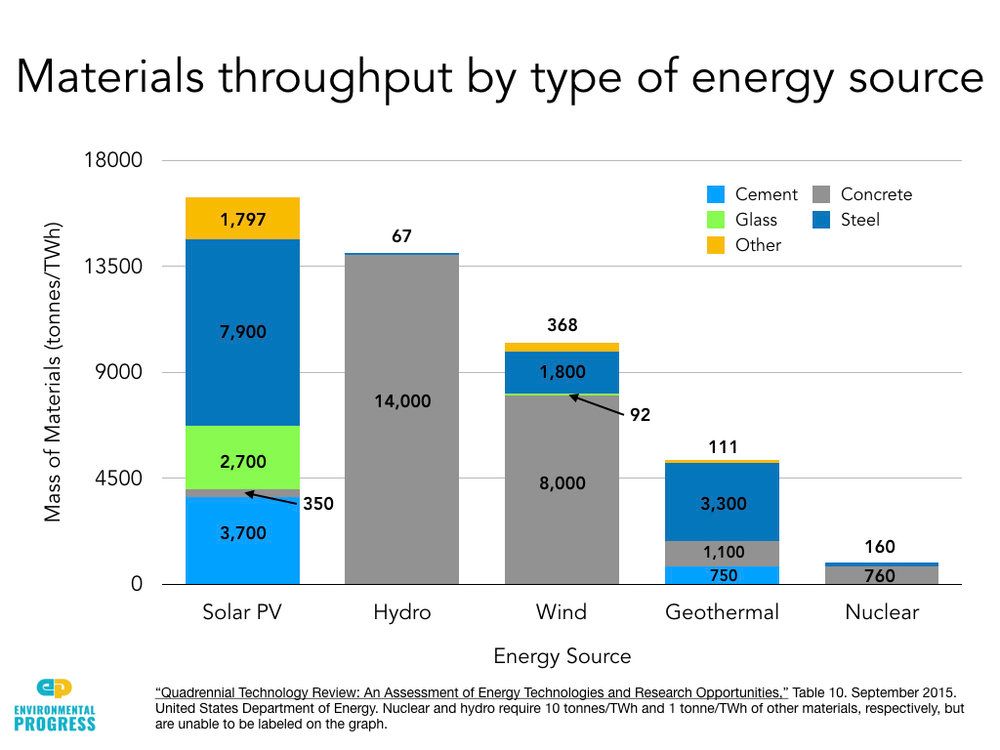
Land and water use – Nuclear power requires far less land than renewables like solar and biofuels. Per unit of energy produced, nuclear uses around 90-100x less land than wind or solar photovoltaics (Ritchie, 2023). However, nuclear does require significant water for cooling. Renewables like wind and solar PV use minimal water in comparison.
Overall, renewable sources like wind and solar PV result in fewer carbon emissions and use less land and water than nuclear energy. However, nuclear has very low emissions compared to fossil fuels, and far smaller land requirements than other renewables. The environmental advantages depend on the specific renewables and metrics compared.
Comparing Costs
When comparing the costs of nuclear power and renewable energy sources like solar and wind, one important metric is the levelized cost of energy (LCOE). The LCOE represents the average cost per unit of electricity generated over the lifetime of the power plant, including construction, fuel, and operating costs.
According to analysis from Lazard, the LCOE for utility-scale solar power ranges from $32-44 per MWh, onshore wind ranges from $26-50 per MWh, and nuclear power ranges from $129-198 per MWh. This suggests that currently, renewable sources like solar and wind tend to have a lower LCOE compared to nuclear power.
However, proponents of nuclear power argue that LCOE comparisons can be misleading. Nuclear plants have very high upfront construction costs, but very low fuel costs over decades of operation. Analyses that discount future fuel costs make nuclear energy appear more expensive. There are also cost advantages to nuclear’s ability to provide reliable baseload power.
Nevertheless, recent constructions of nuclear plants in the U.S. and Europe have seen large cost overruns. Renewable energy costs have also declined rapidly. Most experts agree that currently, renewable energy sources like wind and solar tend to be more cost-competitive than nuclear power in many markets.
Conclusion
In summary, renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal and biomass offer environmental benefits over nuclear power, which creates radioactive waste. Renewables are also becoming cost competitive with nuclear energy. However, nuclear provides steady baseload power while renewables can be intermittent. There is no definitive answer on whether renewable energy is better than nuclear, as each has its advantages. The ideal energy mix likely includes a balanced combination of renewables and nuclear, as this takes advantage of their complementary strengths. More research is still needed to increase renewable capacity and storage solutions. But the future points toward a greater emphasis on clean energy sources like renewables and nuclear over fossil fuels.