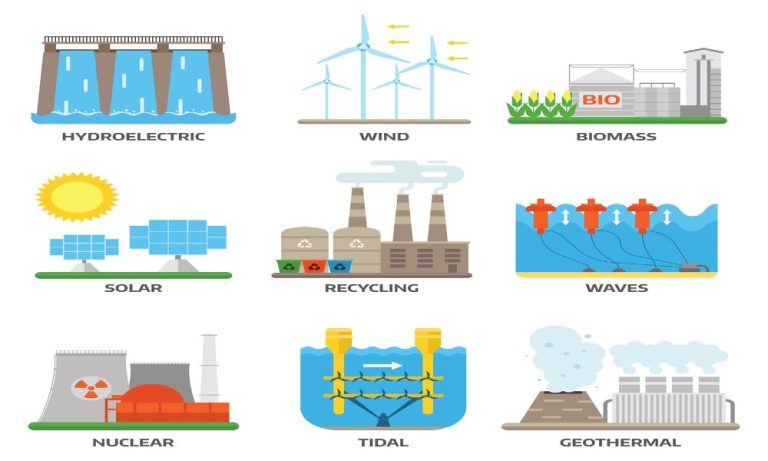
Is Renewable Energy A Fossil Fuel
As the world continues to grapple with the effects of climate change, renewable energy has emerged as a key solution. This form of energy, derived from natural sources such as wind and solar power, is seen as a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuels like coal and oil. While there is no doubt about the benefits of using renewable energy for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainability, there are still lingering questions about its long-term viability compared to fossil fuels. In this blog post, we will dive into the ongoing debate: is renewable energy truly a viable replacement for fossil fuels? We will explore both sides of the argument and weigh in on whether or not we can fully transition away from our dependence on non-renewable resources. So let’s delve in and examine whether renewable energy is truly capable of overtaking fossil fuels as our primary source of power.
Renewable Doesn’T Mean Endless
While renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power have been touted as sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels, it is important to remember that they are not endless resources. For example, solar panels have a typical lifespan of around 25 years, while wind turbines require periodic maintenance and replacement of components such as the blades and gearbox. Additionally, hydroelectric dams can impact local ecosystems and are limited by the availability of water.
Moreover, while renewable energy sources do not emit greenhouse gases during operation like fossil fuels, their production and disposal can have significant environmental impacts. For instance, solar panels and wind turbines require the mining of raw materials such as rare earth metals, which can have negative effects on local communities and contribute to soil and water pollution. Furthermore, the recycling of these components can be complex and energy-intensive.
Despite these challenges, renewable energy has the potential to play a significant role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. Advances in technology have made wind and solar power increasingly efficient and cost-effective, and the adoption of energy-efficient practices can further reduce our overall energy consumption.
Solar Has Limits Too
Solar energy is often considered a key player in the transition towards sustainable energy due to its ability to harness the power of the sun. However, it is important to acknowledge that solar energy also has its limits. One of the primary limitations of solar energy is its reliance on sunlight. Cloudy days and nighttime can significantly impact the amount of energy that can be generated using solar panels. Additionally, solar panels require a relatively large surface area to be effective, which can limit their deployment in urban areas and regions with limited space.
Furthermore, the production and disposal of solar panels can have significant environmental impacts. The manufacturing process of solar panels involves the use of hazardous materials, such as silicon tetrachloride and hydrofluoric acid, which can harm human health if not handled properly. In addition, the disposal of solar panels can pose challenges due to the toxic substances they contain, such as lead and cadmium, which can leach into soil and water if not disposed of properly.
Moreover, solar panels have a typical lifespan of around 25 years, after which they need to be replaced and disposed of. This creates a significant amount of waste and raises concerns about the sustainability of the disposal process. Recycling solar panels can also be a complex and energy-intensive process due to the need to separate different components and materials.
Despite these limitations, solar energy continues to be a promising alternative to fossil fuels. The development of new technologies, such as solar paint and solar windows, could potentially make solar energy more widely available and increase its efficiency. Additionally, the adoption of energy-efficient practices and the integration of energy storage systems could further increase the viability of solar energy as a primary source of power.
Wind Power Isn’T Always Blowing
While solar energy has its limitations, wind power is also not the perfect solution to the world’s energy problems. One of the primary concerns with wind power is its inconsistency. Wind speed and direction are highly variable, resulting in fluctuations in the amount of energy generated. In fact, wind turbines only generate energy when the wind speed is between 6 and 55 miles per hour, with the sweet spot being between 25 and 35 miles per hour. This means that there must be a backup energy source in place to supplement wind power during periods of low wind speeds.
Another issue with wind power is its impact on wildlife. Birds and bats are at risk of collision with wind turbines, which can result in injury or death. Additionally, wind turbines can disrupt the migration patterns of birds, potentially causing long-term damage to populations.
The construction of wind turbines can also have negative environmental impacts. The production of wind turbine parts, such as the blades and towers, generates a significant amount of carbon emissions. The installation of turbines also requires a significant amount of land, which can result in habitat destruction and fragmentation. Additionally, the transmission lines needed to transport wind energy to homes and businesses can cause additional habitat disruption.
Despite these challenges, wind power remains a promising alternative to fossil fuels. Advances in technology are making wind turbines more efficient and cost-effective, and efforts are being made to minimize their impact on wildlife and the environment. For example, new turbine designs are being developed to reduce the risk of bird and bat collisions, and offshore wind farms are being constructed to reduce their impact on land-based habitats. With ongoing research and development, wind power has the potential to become a more reliable and sustainable source of energy for the future.
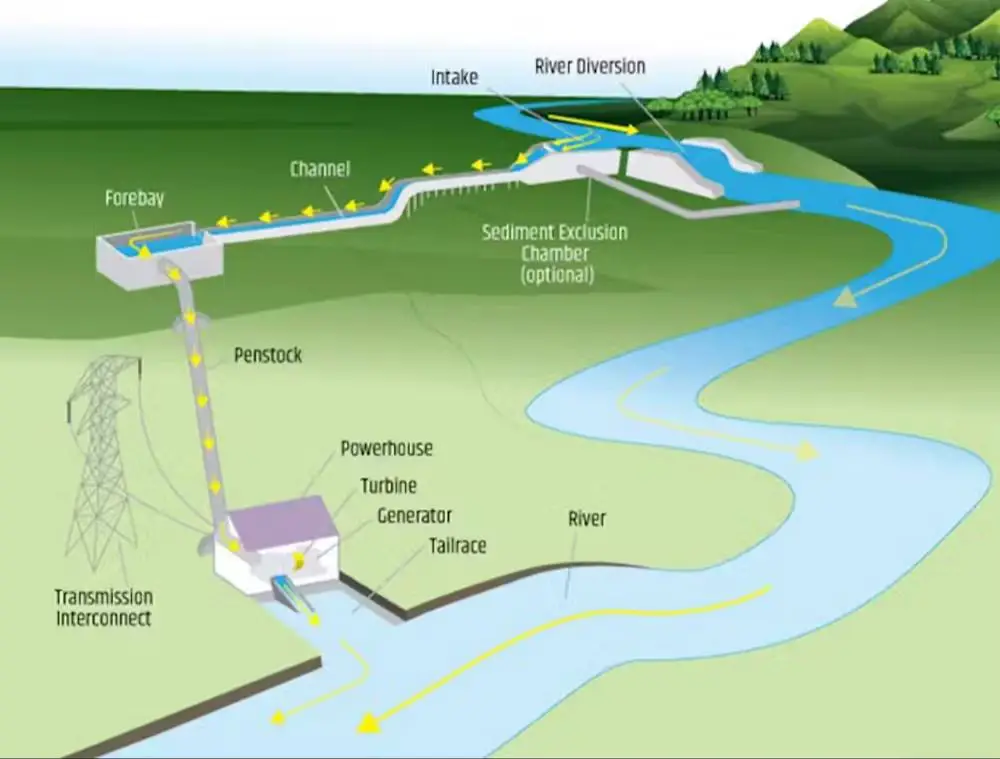
Hydro Needs Water Flow
In addition to solar and wind power, hydroelectric energy is another form of renewable energy that has gained significant attention over the years. This form of energy is generated by tapping the kinetic energy of moving water to produce electricity. While hydroelectric power has proven to be a reliable and cost-effective form of renewable energy, it also has its limitations.
One of the main requirements for generating hydroelectric power is a consistent and steady flow of water. Droughts and other weather-related events can significantly impact water flow, resulting in a decrease in hydroelectric power generation. Even smaller changes in water flow can have a profound impact on power generation, as the efficiency of hydroelectric generators is highly dependent on consistent water flow rates.
Another concern related to hydroelectric power is its impact on ecosystems. Large dams used for hydroelectric power generation can significantly alter river systems, leading to habitat disruption and fragmentation that can ultimately reduce biodiversity. The construction of dams can result in the loss of land, the displacement of communities, and destruction of historical sites and cultural heritage.
Despite these concerns, hydroelectric power remains a significant source of renewable energy and a cornerstone of many countries’ energy infrastructure. In fact, hydroelectric power accounts for approximately 16% of the world’s electricity generation. Additionally, there are efforts underway to mitigate the environmental impact of hydroelectric power, such as the construction of fish ladders to facilitate the migration of fish, and the implementation of water flow management strategies to reduce the environmental impact of dams.
Overall, hydroelectric power is a significant source of renewable energy that requires a consistent flow of water to be utilized effectively. While it has some limitations and potential negative impacts on ecosystems, it remains a vital component of our renewable energy infrastructure and should continue to be developed and refined in a sustainable and responsible manner.
Geothermal Taps Hot Spots
In addition to solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, geothermal energy is another promising form of renewable energy that has shown great potential. Geothermal energy taps into the earth’s natural heat, using steam and hot water reservoirs found in hot spots to generate electricity and heat buildings.
One of the key advantages of geothermal energy is that it produces very little greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. Additionally, geothermal energy is highly reliable, as the hot spots that are used for energy generation do not run out of heat like other renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power.
Geothermal energy has already been deployed in many countries, including the United States, Iceland, and Italy. In the United States, geothermal energy accounts for approximately 3% of the country’s electricity generation, and in Iceland, it is the primary source of energy for heating buildings and generating electricity.
Furthermore, geothermal energy has the potential to provide power to remote and off-grid areas, which are currently dependent on diesel generators for their energy needs. This could significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels and improve energy access for communities in remote regions.
However, the development of geothermal energy is not without challenges. One of the main obstacles is that hot spots are not evenly distributed around the world, limiting its potential for widespread use. Additionally, the drilling required to reach geothermal reservoirs can be expensive and technically challenging.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of geothermal energy make it a promising form of renewable energy that should be further developed and researched for its sustainable and responsible use. As technology continues to advance and new innovations are developed, geothermal energy may become a more significant player in the global energy mix.
All Technologies Have Caps
While geothermal energy offers numerous advantages over fossil fuels and other renewable energy sources, it is important to acknowledge its limitations as well. Like all technologies, geothermal energy has its caps, and it may not necessarily be the silver bullet to solve all energy-related issues.
One of the primary limitations of geothermal energy is its dependence on the availability of geothermal reservoirs. As mentioned earlier, these hot spots are not evenly distributed around the world, limiting the potential for widespread use. This means that some regions may not have access to geothermal energy at all, while others may have to drill deeper and at higher costs to reach the available hot spots.
Furthermore, even in regions where geothermal reservoirs are abundant, the drilling and development of geothermal power plants can be technically challenging and expensive. This can pose a significant barrier to entry for some developers, especially those who lack the necessary technical expertise or financial resources to undertake such projects.
Another limitation of geothermal energy is its potential impact on the environment. While geothermal is considered a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels, the drilling, and development of geothermal power plants can have adverse effects on the surrounding ecosystem. For instance, the drilling process can cause seismic activity or affect underground water supplies.
Moreover, the exploration and exploitation of geothermal reservoirs may have cultural and social implications on local communities, especially if they are not consulted or adequately compensated for the use of their land. This can lead to tensions between developers and local communities, and even resistance to geothermal energy projects.
Saving Energy Extends Supply
Saving energy offers a crucial solution to ease the current demand for energy, and extend the supply of non-renewable resources. With the incorporation of energy-efficient technology and practices, individuals can significantly reduce their energy consumption while still meeting their daily needs. Additionally, saving energy can lead to substantial monetary savings over the long-term, as people consume less power and pay lower energy bills.
Furthermore, the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can also play an essential role in extending our energy supply. As technology advances, renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly cost-effective, making this transition financially feasible for many individuals and businesses. By embracing renewable energy sources, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the negative impact of greenhouse gas emissions on the environment.
Investing in energy-saving initiatives and renewable energy infrastructure presents enormous economic benefits as well. These include numerous job opportunities that come with the development and maintenance of renewable energy projects. Similarly, energy-efficient retrofits can spur economic growth by providing jobs in the construction and maintenance of energy-efficient buildings and homes.
Embracing energy-saving measures and renewable energy is vital to combatting climate change and protecting the environment. By adopting these practices, we can ensure not only the longevity of our energy supply but also a more sustainable and livable planet for future generations.
Adapting Uses Less Overall
Adopting energy-saving measures presents a crucial solution to meet our energy needs while reducing our dependency on non-renewable resources. By incorporating energy-efficient technologies and practices, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce their energy consumption without sacrificing their daily needs. This reduction in consumption results in a slower exhaustion of finite non-renewable resources, significantly extending the longevity of our energy supply.
Moreover, embracing renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, can further supplement our energy supply while reducing our reliance on finite non-renewable resources. The cost-effectiveness of renewable energy is consistently improving as technology advances. This shift towards renewable energy sources makes it financially feasible for individuals and businesses alike to adopt energy-saving initiatives and renewable infrastructure. The environmental benefits of transitioning to renewable sources more than justify the initial investment and present enormous economic opportunities for job creation in the development and maintenance of renewable energy projects.
Not only does this transition towards renewable and sustainable energy sources reduce our carbon footprint, but it also promotes economic growth through job creation opportunities. The development and maintenance of renewable energy projects create numerous job opportunities, and energy-efficient retrofitting projects can create jobs in construction and maintenance. Therefore, adopting energy-saving measures and renewable energy sources presents a comprehensive solution to combat climate change, promote sustainability, and create economic opportunities for everyone.
Overall, conserving our energy resources and adopting renewable energy sources is vital to ensuring a more sustainable future for everyone. By adopting these measures, we can guarantee not only the longevity of our energy supply but also a better and healthier planet for future generations.
Conserving Our Shared Reserves
Conserving our shared reserves of non-renewable resources is an imperative for the long-term security of our energy needs. Currently, global energy consumption is largely dependent on non-renewable resources such as coal, oil, and natural gas, which are finite and non-sustainable. The overreliance on these resources is jeopardizing the future of our planet and posing existential threats to the world’s most vulnerable populations.
Experts predict that we will experience a severe energy crisis in the near future if we do not take appropriate measures to conserve our resources. This crisis will undoubtedly affect our economy, national security, and the overall quality of life for billions of people worldwide. In contrast, renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and geothermal power have the potential to provide a sustainable solution to our energy needs.
The transition to renewable energy sources offers multiple environmental and economic benefits. Renewable energy is a cleaner and more sustainable source of energy, resulting in fewer harmful carbon emissions and reducing our carbon footprint. Solar and wind power plants have significantly lower operating costs, reducing the long-term cost of energy and creating job opportunities in the development and maintenance of renewable energy infrastructure.
Another crucial aspect of conserving our shared reserves is the responsible management of freshwater resources. Approximately 70% of the world’s freshwater is used for agricultural purposes, meaning that efficient water usage will be a critical factor in addressing energy scarcity, particularly in drought-prone areas.
Conserving our shared reserves of non-renewable resources necessitates comprehensive policy interventions and individual actions. Raising awareness about energy conservation practices, increasing investments in renewable energy, and optimizing resource use efficiency should be given top priority. Additionally, allocating resources to research and development of clean energy technologies will enable us to better address present and future energy challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is evident that while renewable energy sources offer numerous advantages over traditional fossil fuels, they are not without their limitations. From solar energy’s dependence on sunlight to wind power’s reliance on favorable weather conditions, it is clear that we cannot solely rely on these resources to meet our energy needs in the long run. As we continue to explore and invest in alternative energy solutions, it is important to keep in mind that all technologies have caps and we must actively work towards conserving them to extend their lifespan. By saving and adapting our energy usage, we can not only decrease our dependence on non-renewable sources but also reduce the strain on our shared reserves. It is crucial for us to think beyond just finding new energy sources and instead consider how we can use less overall. Only through a combination of conservation and investment in renewable options can we truly make a significant impact in preserving our planet for future generations. So let us all take action now and do our part in ensuring a sustainable future for all. Together, we can build a brighter future where renewable truly means endless possibilities for generations to come.