Is Electric The Same As Hydro?
Electric and hydro power are two of the main sources for producing energy around the world. They each have their own advantages and disadvantages when it comes to efficiency, cost, environmental impact, and usage.
The goal of this article is to clearly explain what electric and hydro power are, compare and contrast them, and provide readers with a deeper understanding of the differences between these two important methods for generating electricity.
What is Electric Power?
Electric power refers to the generation of electricity and its transmission via an interconnected system called the grid. The generation of electricity can come from various sources, such as fossil fuels like coal, natural gas, and oil, nuclear power, or renewable sources like hydro, wind, solar, geothermal, and biomass. At power plants, the potential energy stored in these fuel sources is converted into electrical energy. This electricity is distributed through transmission and distribution lines that make up the power grid. The voltage is stepped up by transformers as power is transmitted over long distances. Then, the voltage is reduced and electricity is supplied to homes, businesses, and industries through distribution lines. Electric power is essential to modern life, from lighting and appliances to communications, manufacturing, and infrastructure. An accessible, reliable electric grid is crucial for economic development.
What is Hydro Power?
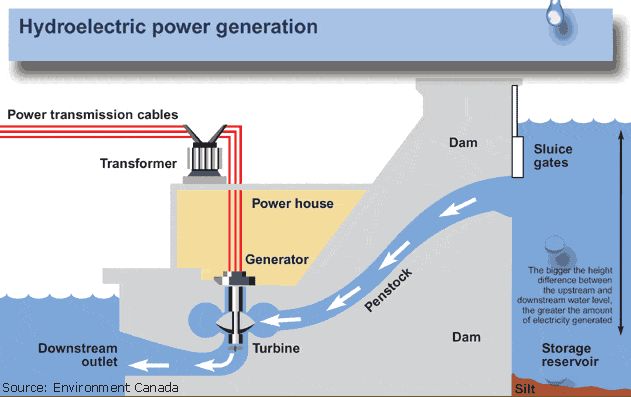
Hydro power, also known as hydroelectric power, refers to the process of generating electricity through the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water. It is one of the oldest and most widely used renewable energy sources in the world.
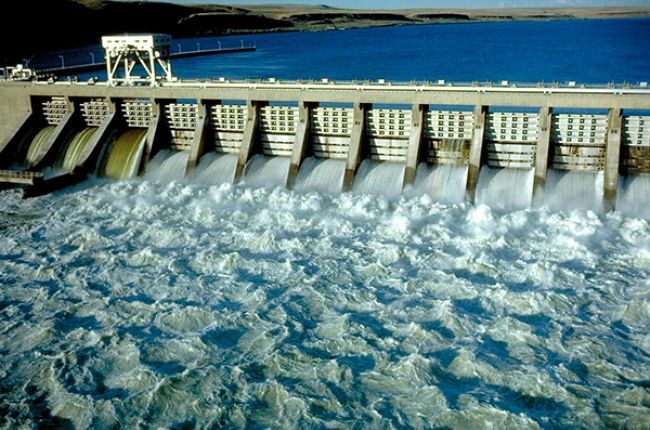
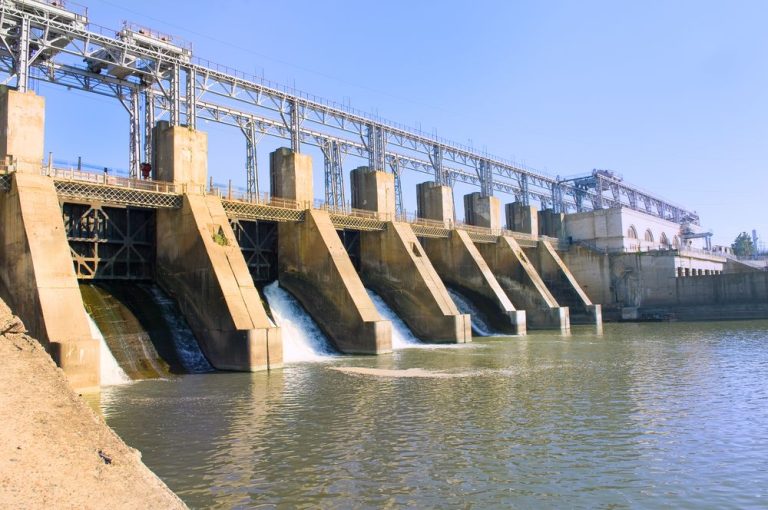
The most common type of hydro power plant uses a dam on a river to store water in a reservoir. The water flows through a turbine, causing it to spin. The motion of the turbine spins a generator to produce electricity. The amount of electricity that can be generated depends on the volume of water flow and the height from which it falls.
Run-of-river hydro plants channel a portion of a river through a canal and then through turbines to generate electricity. This type of hydro plant captures energy from the natural flow of the river without the need for dams and reservoirs.
Overall, hydro power is an efficient, renewable, and clean energy source that provides around 16% of the world’s electricity. It offers flexibility to meet peaks and troughs in electricity demand as the power output can be adjusted rapidly. Hydro power facilities also often serve as multi-purpose projects, providing flood control, irrigation, and recreation.
Similarities Between Electric and Hydro
Although electric power and hydro power utilize different energy sources, they share some key similarities in how they generate electricity. Both rely on turbines that are spun by the energy source to rotate electromagnets within a generator. This movement of the magnets induces a flow of electrons, creating alternating current electricity. The electricity generated is connected to the power grid and distributed for residential, commercial and industrial use.
While hydro power uses the kinetic energy from flowing or falling water to turn the turbines, electric power stations use the heat energy from coal, natural gas, nuclear fission, or other fuel sources to convert water into high-pressure steam that spins the turbine. Despite the different energy sources, both produce rotational mechanical energy that gets converted into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
So in summary, both hydroelectric and electric power plants generate electricity for the grid using turbines that are spun by an energy source to rotate magnets within an electricity generator.
Differences Between Electric and Hydro
One key difference between electric and hydro power is the diversity of energy sources used to generate electricity. Electric power can utilize a variety of sources including coal, natural gas, nuclear, solar, wind, geothermal, and biomass. This means electric power generation has more flexibility in terms of fuel sources.
In contrast, hydro power is generated solely from flowing water. Giant dams are built to control water flow and the kinetic energy from the moving water spins large turbines to produce electricity. Hydro power relies entirely on water sources and sufficient water flow levels.
Another major difference is the infrastructure required. Electric power from sources like coal and nuclear require large power plant facilities connected to transmission lines that distribute the electricity. Solar and wind power require solar panels or wind farms plus infrastructure to connect to the grid.
Hydro power requires the construction of dams, reservoirs, turbines and generators plus transmission lines. So the infrastructure investment for hydro power is focused on dams and waterways rather than multiple power plants.
In summary, a key distinction is that electric power has more diversity in fuel sources while hydro power depends solely on water flow for its generation capacity.
Efficiency Comparison
When comparing the efficiency of electric and hydro power, hydro power is generally much more efficient. This is because hydro power makes use of the natural flow of water, with little energy loss in the process. Hydroelectric generators can convert as much as 90% of the available energy into electricity.
The efficiency of electric power generation can vary greatly depending on the fuel source. Fossil fuel plants like coal, gas and oil have an average efficiency around 50%. Nuclear power plants can reach over 90% efficiency. And renewable sources like solar and wind have variable efficiency rates depending on conditions and technology used.
So in summary, hydro power is a very consistent and efficient renewable source. Electric power efficiency can range widely depending on the generation method. But hydro clearly exceeds the efficiency of most electric generation like that from fossil fuels.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of electric power generation varies depending on the source. Fossil fuel plants produce air pollution and greenhouse gases. Nuclear plants have waste disposal challenges. Renewables like solar and wind have lower impacts once built.
Hydroelectric dams and reservoirs drastically change river environments flooding large areas upstream. This alters natural water flows and fish migration patterns. Large dams block sediments causing increased erosion downstream. Reservoirs increase greenhouse gas emissions from rotting vegetation. Hydro facilities disrupt natural habitats and can require relocating human populations.
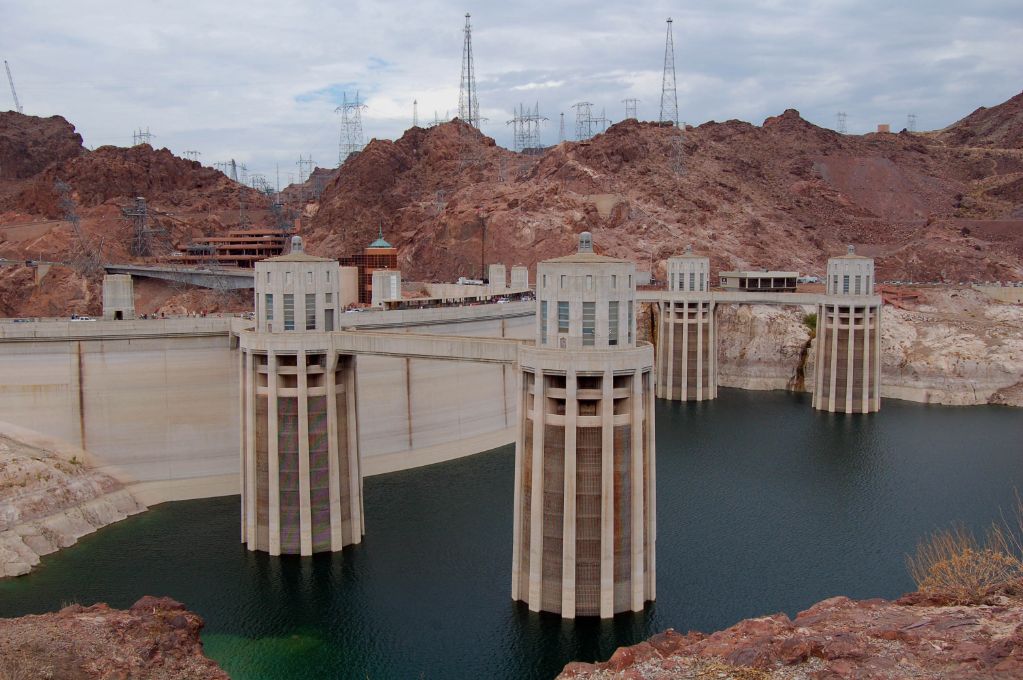

Overall, hydroelectric power has a much more direct impact on local environments than most electric power sources. Electricity from fossil fuels, nuclear, solar or wind can be generated in remote areas far from populations. But large hydro dams cause permanent disruption to rivers near inhabited regions.
Cost Comparison
When considering the overall costs, hydro power is generally less expensive than electric power from other sources. This is because once a hydroelectric dam and power plant is constructed, the fuel source (flowing water) is free. There are some maintenance costs, but no fuel costs. Electric power plants powered by coal, natural gas, oil, or nuclear require ongoing expenditures for their fuel.
The cost of generating electric power depends greatly on the fuel source. Coal and natural gas tend to be the least expensive. Building and operating a nuclear power plant is very capital intensive. Renewable sources like solar, wind, and geothermal can vary in cost depending on the technology.
So while hydro power plants are expensive to construct initially, their lack of fuel costs makes them cost effective over the long run. The range of costs for other electric power sources depends on many factors. But hydro generally has lower overall costs compared to fossil fuels and nuclear.
Usage by Region
Hydro and electric power generation methods are used in different capacities around the world. Some regions utilize hydro power more extensively while electric power tends to be more widespread globally.
Hydro power is prominent in regions with ample water resources like rivers, waterfalls, and dams. Countries such as Canada, Brazil, and Norway generate a high percentage of their electricity from hydro plants. For example, hydro supplies roughly 60% of electricity generation in Canada.
Electric power covers a broader geographic range. While hydro is limited by water resource availability, electric generation can utilize various power sources. Electric plants may run on fossil fuels like coal and natural gas or renewable sources such wind and solar. This flexibility allows electric power to meet demand in most regions of the world.
Overall, electric power capacity exceeds hydro capacity globally. As of 2018, hydro accounted for 16% of global electricity generation while fossil fuels and other electric sources made up the remaining 84%. While hydro output is concentrated in select world regions, electric power has a nearly ubiquitous presence.
Conclusion
To summarize, hydro power and electric power share some similarities in that hydro power is one way of generating electricity. However, they differ in that hydro power specifically refers to generating electricity by harnessing the power of moving water, while electric power more broadly refers to generating electricity through various means, including sources like fossil fuels, solar, wind, and nuclear in addition to hydro power.
While both hydro and other forms of electric generation have their pros and cons, hydro power is renewable, relatively low impact on the environment, and cost effective once facilities are constructed. However, it is dependent on suitable geography and water sources. Other electric generation methods like nuclear and fossil fuels can be implemented virtually anywhere but have waste and emissions drawbacks.
So in conclusion, hydro power is one form of electric generation but not the only one. When comparing energy sources, factors like renewability, location, upfront costs, and environmental impact must be weighed.