How Much Energy Do You Save With Led?
Incandescent light bulbs have been the standard lighting source for over a century, but LED (light-emitting diode) bulbs are quickly becoming more popular. LED bulbs are highly energy efficient compared to traditional incandescents. An LED bulb can use up to 90% less energy than an equivalent incandescent bulb and last 25 times longer, leading to significant cost savings over time.
Incandescent bulbs work by heating a tungsten wire filament until it glows and produces light. This process is inefficient, since most of the energy is given off as heat. LEDs produce light through electroluminescence, requiring far less electricity. This difference in operation leads to massive energy savings when using LED bulbs instead of incandescents.
Wattage Difference
LED bulbs require significantly less wattage than traditional incandescent bulbs to produce the same amount of light. An incandescent bulb works by heating a filament wire to a high temperature until it glows and emits light. This process is very inefficient, resulting in most energy being converted to heat rather than visible light. In contrast, LEDs (light emitting diodes) produce light directly through electroluminescence, allowing over 80% of energy to be converted to light rather than heat [1].
As an example, a 60W incandescent bulb that emits 800 lumens requires 60 watts of electricity. An equivalent LED bulb that emits the same 800 lumens uses only 8-12 watts [2]. This represents around an 80% reduction in wattage and energy usage. Across larger lighting installations, these wattage differences can lead to substantial energy savings over time.
Lumens Produced
Lumens are a measure of the total amount of visible light emitted by a light source. In LED lighting, lumens measure the brightness of a light. This is different than Watts, which measure the amount of energy in a light. The term lumens refers to the flux, or flow of light emitted in all directions from a source. The more lumens, the brighter the light.1
For LED bulbs, knowing the lumens rating gives you an idea of how bright the light will be. For example, here are some typical lumens for different LED bulbs:2
- 40-watt equivalent LED bulb: 450 lumens
- 60-watt equivalent LED bulb: 800 lumens
- 75-watt equivalent LED bulb: 1,100 lumens
- 100-watt equivalent LED bulb: 1,600 lumens
So when choosing an LED bulb, pay attention to the lumens rating to understand the brightness, rather than focusing just on the wattage equivalent.
Lifespan Difference
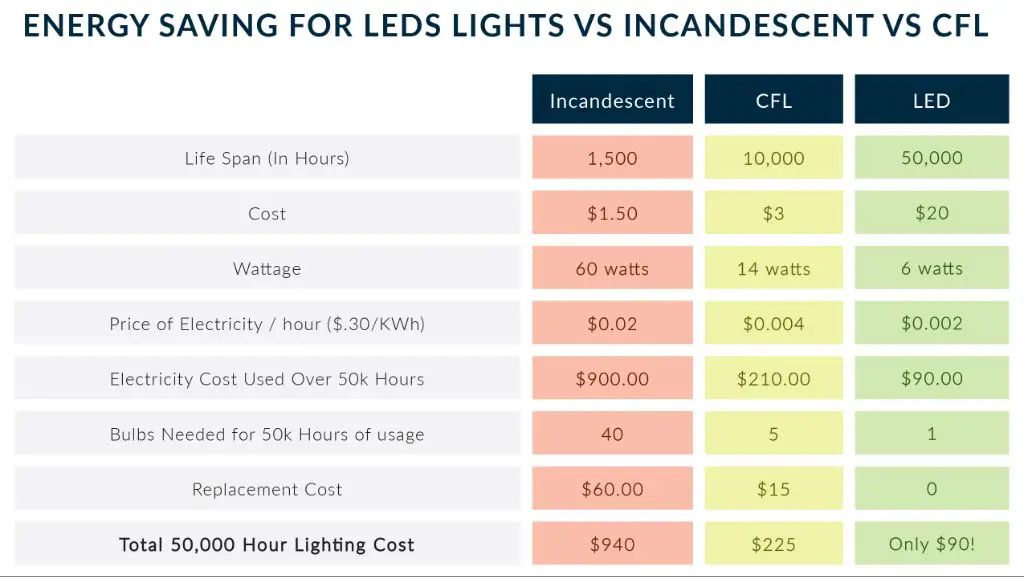
There is a significant lifespan difference between incandescent, CFL, and LED bulbs. Incandescent bulbs last only around 1,000 hours, while LED bulbs last up to 50-100 times longer at around 50,000 hours or more.
This source
explains that incandescent bulbs usually last for 750 to 1,000 hours, CFL bulbs for 8,000 to 10,000, and LED bulbs for at least 25,000 and up to 50,000 or even 100,000 hours. So incandescent bulbs are extremely short-lived compared to LEDs. While CFLs last much longer than incandescents, LEDs still outlast them 5-10 times over.
The significantly longer lifespan of LED bulbs means you have to replace them far less frequently. Instead of replacing bulbs multiple times a year with incandescents, LEDs can easily last over a decade before needing to be swapped out.
Heat Produced
LED lights produce far less heat than incandescent bulbs. Incandescent bulbs work by heating a tungsten wire filament to very high temperatures until it glows and emits light. This process is extremely inefficient, with only around 5% of the energy consumed converted into visible light. The other 95% is wasted as heat. In contrast, LEDs produce light via electroluminescence which is far more efficient at converting electricity into light. As a result, LED bulbs generate very little heat in comparison. One test found that after being on for 2 hours, an LED bulb was just warm to the touch while an incandescent bulb was too hot to touch (Lifx). The lack of heat from LEDs also makes them safer and able to be used in more enclosed fixtures.
Energy Cost Savings
Switching from traditional incandescent bulbs to LEDs can result in significant energy and cost savings. LEDs consume up to 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs and last up to 25x longer (Midstream Lighting). This translates into major reductions in electricity costs over time.
One key factor is wattage – an incandescent 60W bulb can be replaced by an LED that uses just 8-12W. For a single bulb, this can save around $5 per year in electricity costs. But when scaled up for a full home or commercial building with hundreds of bulbs, the savings really add up. It’s estimated LEDs can cut lighting electricity costs by 50-80% (LampHQ).
Online LED savings calculators can provide estimates based on your specific energy costs, hours of use per day, and number of bulbs. For many homes and businesses, switching entirely to LEDs can save hundreds or even thousands per year in lower electricity bills (Novel Energy Lighting). Those savings typically pay back the upfront cost of new LED bulbs within just 1-3 years.
Environmental Impact
LED lights have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. According to Hilclare, LEDs conserve up to 80% more energy than fluorescent and incandescent lighting (https://hilclare.com/leds-are-better-for-the-environment-earthday-2021/). This major reduction in energy usage leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions from power plants. UK Energy Lighting explains that LEDs require very little power, meaning less fuel needs to be burned to generate electricity (https://ukenergylighting.co.uk/how-does-led-lighting-help-the-environment/). The US Department of Energy estimates that widespread use of LEDs over the next 20 years could save the United States $250 billion in energy costs and prevent 1,800 million metric tons of carbon emissions. Clearly, LED lighting is significantly better for the environment by reducing pollution and minimizing our carbon footprint.
Downsides of LEDs
While LED lights have many advantages, there are some downsides to consider as well. One of the main disadvantages of LEDs is their higher upfront costs compared to incandescent or CFL bulbs. An LED bulb can cost $10-15, whereas an incandescent bulb may only be $1-2. However, LED bulbs have a much longer lifespan, so the cost savings accumulate over time (https://www.bebrilli.com/blogs/brilli/pros-and-cons-of-led-lights).
There are also some concerns about light quality with LEDs. Early LED bulbs had issues with color accuracy and creating glares. Modern LED bulbs have improved significantly in these areas, but some people still prefer the warm, omnidirectional light that incandescent bulbs provide (https://www.destinationlighting.com/fliptheswitch/led-pros-and-cons/). LEDs also emit more blue light than incandescent bulbs, which some worry could disrupt sleep patterns if used before bed.
When to Choose LEDs
LED lightbulbs are a great option in many circumstances, but not necessarily right for every lighting application. Here are some recommendations for when LEDs make the most sense:
– Any fixture where the bulb is difficult to access and change frequently. Since LEDs last so much longer than incandescent and CFL bulbs, they make sense in hard-to-reach fixtures where bulb changes are a pain.
– Outdoor lighting and lamps exposed to weather or vibration. LEDs hold up better than other bulb types in these conditions.
– Rooms where lights are on for many hours per day. The long lifespan and energy efficiency of LEDs maximize savings in these high-use situations.
– Dimming applications. LEDs perform better than incandescents and CFLs when dimmed.
– Accent and track lighting. The directional nature and small size of LEDs make them perfect for these fixture types.
– Places where lighting quality matters like kitchens and workspaces. LEDs provide better light quality than incandescent or CFL bulbs.
– Situations where you want smart lighting capabilities like color changing or connectivity. LED bulbs offer the most options for smart features.
– New construction or renovation projects. Installing LED fixtures and bulbs from the start maximizes long term savings and avoids future bulb replacements.
Conclusion
Switching to LED lighting is one of the easiest ways to start saving energy at home. As we’ve seen, LED bulbs use at least 75% less energy and last up to 25 times longer than traditional incandescent bulbs. They also produce 90% less heat, which further reduces energy usage from cooling. The energy savings from LEDs can quickly add up, reducing electricity bills and carbon footprints. With continuing improvements in light quality and falling prices, there’s little reason not to switch most of your home’s lighting over to LEDs. Doing so is one of the most accessible steps we can take towards energy efficiency and sustainability.