How Many Kw Is 400W Solar Panel?
Solar panels generate electricity by converting sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. The wattage of a solar panel indicates how much power it can produce under ideal conditions. A 400W solar panel can generate 400 watts of DC power when pointed directly at the sun on a clear day.
To properly size a solar panel system for a home or business, it’s important to understand how to convert watts to kilowatts (kW). While solar panel wattage is measured in watts, most electricity usage is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). By converting watts to kilowatts, you can calculate how many solar panels you need to meet your energy needs.
Definition of Watts and Kilowatts
A watt is a unit of power that measures the rate of energy transfer. A watt measures how fast electricity is being used or produced at any given moment.
For example, a 100-watt light bulb uses 100 watts of electricity to produce light. The higher the wattage, the faster energy is being transferred to power the device.
A kilowatt (kW) is equal to 1,000 watts. It’s a larger unit of power commonly used to measure electricity usage for appliances, equipment, and wiring systems.
For example, a typical household might use 700-900 kilowatts of electricity per month. Kilowatts are useful for measuring the output of large-scale power sources like power plants and solar panel systems.
Wattage of Common Household Appliances
When sizing a solar panel system, it’s helpful to understand the wattage requirements of common household appliances and devices. This provides a frame of reference for how much power typical items draw. Some examples of wattages for everyday appliances include:
- Refrigerator – 500-800 watts
- Clothes washer – 350-500 watts
- Dishwasher – 1200-2400 watts
- Microwave oven – 800-1100 watts
- Electric oven – 2000-5000 watts
- Toaster – 800-1500 watts
- Coffee maker – 900-1200 watts
- Hair dryer – 1200-1875 watts
- Ceiling fan – 50-175 watts
- Desktop computer and monitor – 270-400 watts
- Laptop computer – 20-100 watts
- TVs – 100-400 watts depending on size
- Smartphone charger – 5-12 watts
Knowing the wattage requirements for the devices you plan to power with your solar panel system will help determine the size and number of panels needed.
Sizing a Solar Panel System
When sizing a solar panel system for a home or business, there are several key factors to consider:
Electricity Usage – The most important factor is calculating your location’s electricity usage measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Examine previous electric bills to determine monthly and annual usage.
Sun Hours – The solar potential of your area depends on the average peak sun hours per day. More sun equals more electricity generation. Sun hours vary widely by location.
Panel Wattage – With your electricity needs and sun hour potential calculated, you can determine how many watts of solar panels are required. Multiply the kWh requirement by 1000 to convert to watts. Higher wattage panels will take up less physical space.
Physical Space – Consider the physical roof or ground space available for the total square footage of panels needed. Standard solar panels are approximately 65 inches by 39 inches.
Future Growth – It’s smart to size your system beyond your current needs to allow for future electric vehicle charging or appliance upgrades. Ideally a system will meet 80-100% of your kWh usage.
Energy Efficiency – Reducing energy waste with efficient lighting, appliances and weatherization lowers kWh usage, allowing a smaller solar system to meet your electricity demand.
400W Solar Panel Specifications
A typical 400W solar panel will have the following specifications:
- Dimensions: 65 inches x 39 inches x 1.4 inches
- Weight: 47 lbs
- Cells: 144 monocrystalline silicon cells
- Maximum power (Pmax): 400W
- Voltage at Pmax (Vmp): 34.2V
- Current at Pmax (Imp): 11.7A
- Open-circuit voltage (Voc): 44.6V
- Short-circuit current (Isc): 12.6A
- Maximum system voltage: 600V DC
- Operating temperature: -40°F to 185°F
- Maximum series fuse rating: 25 Amps
These specifications provide an idea of the size, voltage, wattage, and electrical output you can expect from a standard 400W solar panel. This helps determine how many panels are needed for a home solar system based on energy requirements. The key factors are the panel wattage, voltage, and amperage ratings.
Converting Watts to Kilowatts
When sizing a solar panel system, it’s important to understand the difference between watts and kilowatts and how to convert between the two units. Watts (W) are a measure of power and kilowatts (kW) are equal to 1,000 watts.
The conversion formula from watts to kilowatts is simple:
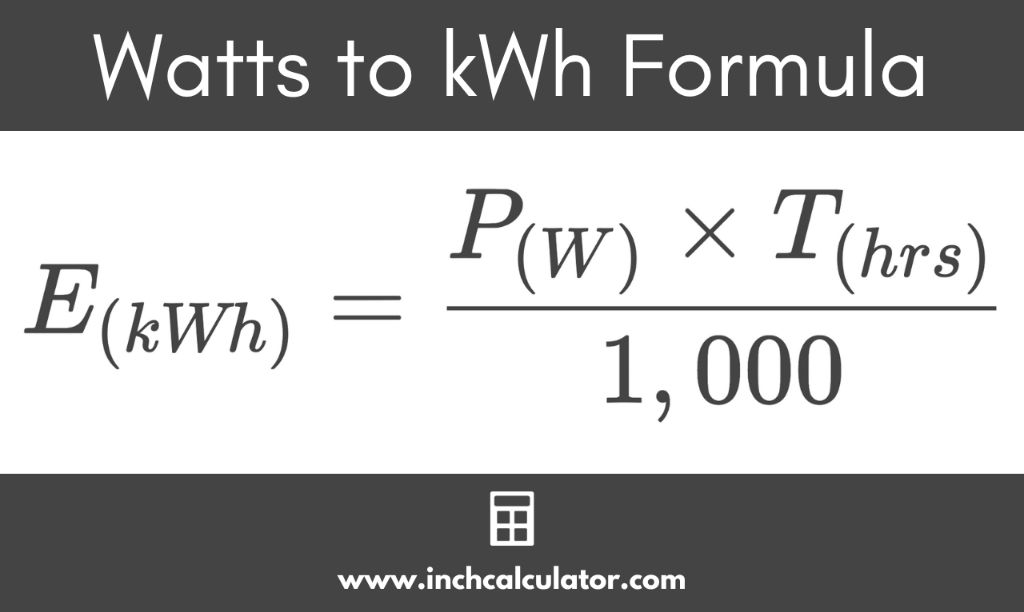
Kilowatts = Watts / 1000
So for example, if you have a 400 watt solar panel, you can calculate the kilowatt rating by taking the watts and dividing by 1000:
400 Watts / 1000 = 0.4 Kilowatts
Knowing how to convert between watts and kilowatts allows you to properly size and compare the capacities of solar panel systems. When determining the number of solar panels needed for a home, the kilowatt rating provides a standard unit of measurement.
Calculating Kilowatts for a 400W Solar Panel
To calculate the kilowatt rating of a 400W solar panel, we simply need to convert watts to kilowatts using basic math.
First, let’s review the definitions:
- 1 watt = 1 joule per second
- 1 kilowatt = 1,000 watts
So to convert watts to kilowatts, we divide by 1,000.
For a 400W solar panel:
400W ÷ 1000 = 0.4kW
Therefore, the kilowatt rating of a 400W solar panel is 0.4kW.
To summarize:
- 400W solar panel
- 1 kW = 1,000 W
- 400W ÷ 1000 = 0.4 kW
So a 400W solar panel converts to 0.4 kilowatts.
How Many 400W Panels for a House?
The number of 400W solar panels needed for an average home depends on several factors like the home’s location, roof size, and energy usage. As a rough estimate, most homes require between 20-40 panels for a full solar installation.
An average home uses about 30 kWh of electricity per day. With 6 hours of good sunlight, 1 square meter of solar panel can produce 4-5 kWh per day. Each 400W solar panel is around 2 square meters in size. So each 400W panel can generate around 8-10 kWh per day.
To cover 30 kWh of daily use, a home would need about 3-4 panels per kWh, which works out to around 90-120 panels. But after losses from system inefficiencies, roof angles, and suboptimal sunlight, that comes down to a typical range of 20-40 panels for the average home.
Homes in sunnier climates or with greater energy needs may require panels on the higher end. Homes with net metering to offset nighttime use may also need a larger system. But in general, installing around 30 x 400W panels, for a 12,000W (12kW) system, should provide enough solar energy for most homes.
Other Factors When Sizing a Solar System
In addition to calculating the number of 400W solar panels needed, there are other important factors to consider when sizing a solar panel system:
Sunlight: The amount of sunlight your location receives will impact how many solar panels you need. Areas with more annual sunlight can generate more electricity with fewer panels. Check solar maps to see sunlight levels in your region.
Geography: Nearby landscapes and structures can cast shadows and block sunlight from reaching panels. Account for obstructions like trees, hills, and buildings when siting your system.
Energy Use: Consider your household’s energy consumption. More energy used will require a larger solar system to meet your needs. Conduct an energy audit to understand your usage.
Panel Orientation: Tilting panels toward the equator maximizes sunlight exposure. Optimal orientation varies by hemisphere and latitude. Proper installation is key.
Weather: Extreme weather like snow, storms, and hail can affect solar production. Have realistic expectations for electrical output in different seasons and conditions.
Considering these other variables will help right-size your solar panel system for maximum efficiency and energy offset.
Conclusion
In summary, a 400 watt solar panel provides 0.4 kilowatts of power. This is enough to run some small appliances and electronics in a home but larger appliances or many devices at once would require more solar panels. When sizing a complete solar system, factors like sun hours, energy usage, panel efficiency, and expandability should be considered along with the wattage. While a single 400W panel can provide useful supplemental power, most homes require an array of multiple panels to meet their energy needs. The number of panels depends on the home’s location and demand. By calculating your home’s needs and combining enough solar panels, you can harness renewable energy from the sun and reduce your environmental impact.