How Is Wind Helpful?
Wind is the movement of air flowing across the planet. Wind is helpful in a variety of ways that make life on Earth possible. In this article, we will explore the ways that wind can be useful and beneficial.
Generating electricity
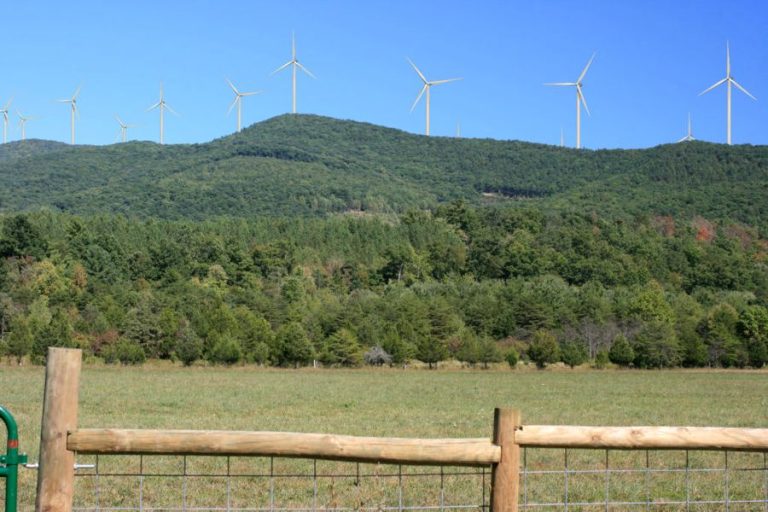
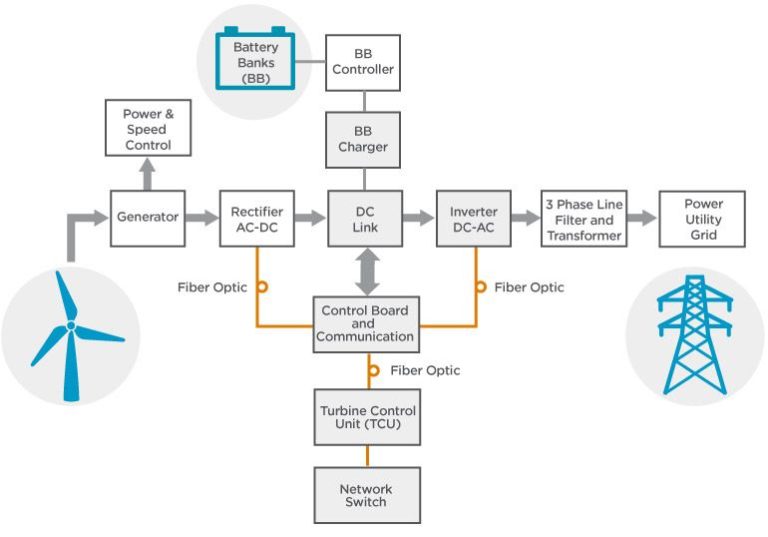
One of the most well-known ways that wind is helpful is in generating electricity through wind turbines and wind farms. Wind turbines harness the power of the wind to turn large blades connected to a rotor. As the blades spin, they turn an internal shaft connected to a generator that converts the mechanical power into electrical power.
Many wind turbines are grouped together in wind farms or wind power plants to generate electricity on a utility scale. The wind blows across the large expanse of land or sea where the wind farm is located and turns many wind turbines simultaneously. In 2020, wind power generated over 300 terawatt-hours of electricity globally, which met over 7% of the world’s electricity demand that year.
Some countries generate an even larger share of their electricity from wind power. For example, wind generated over 40% of electricity in Denmark, around 30% in Ireland and Germany, and approximately 25% in Portugal and Spain in 2020. The United States produced over 300 terawatt-hours of wind power in 2020, representing about 8.4% of total U.S. electricity generation.
Wind power is one of the fastest growing renewable energy technologies worldwide. Many countries have set goals to continue increasing their wind power capacity to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and rely more on clean energy sources.
Propelling ships
One of the most important uses of wind throughout history has been to propel sailing ships. For thousands of years, wind provided the primary means of powering ships across seas and oceans. This enabled exploration, trade, and transportation between different regions of the world.
Sailing ships such as schooners, brigantines, and frigates used large masts with square sails to capture the wind. The design of these tall ships allowed them to efficiently harness the power of the wind to propel them through the water. Skilled crews could angle the sails and rudder to best utilize the available winds.
Before the steam engine, wind served as the only viable energy source for long distance ocean travel. Reliable wind patterns like the trade winds made regular trade routes possible between Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. Economic empires were built upon trading networks spanning continents and oceans.
The Age of Sail brought about unprecedented global connectivity. It facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, culture, and technology between civilizations. Even after the advent of steamships, sailing vessels continued serving economic and recreational purposes. The rich maritime heritage of sailing is still very much alive today.
Cooling Effects
Wind plays an important role in cooling people, animals, and environments by removing heat. On a hot summer day, a light breeze can provide welcome relief from high temperatures. As wind blows across your skin, it increases evaporation of sweat, allowing your body to cool more efficiently. Wind circulation dissipates heat in outdoor and indoor spaces, helping maintain comfortable temperatures.
For many living things, wind helps regulate body temperature within survivable ranges. Animals like elephants use their large ears to disperse body heat. Wind through vegetation moderates the climate of forests and jungles. Proper ventilation prevents indoor spaces like barns and chicken coops from overheating. Fans and air conditioning rely on the cooling effects of moving air.
At a larger scale, wind currents transport heat from equatorial regions toward the poles. This acts as a critical climate control mechanism for the planet. Wind systems maintain a balance between colder and warmer global zones. Without this redistribution of heat, equatorial areas would be too hot while polar climates would grow extremely cold. The global conveyor belt of wind and ocean currents regulates Earth’s temperature for the benefit of all life.
Wind Energy
Humans have harnessed the power of wind for thousands of years. The earliest known use was in sailing, where the wind propels ships across bodies of water. This allowed ancient civilizations to explore, trade, and migrate across the seas. Even today, sailing ships harness the wind for propulsion.

Another early use of wind power was through windmills. Windmills consist of large vanes or sails attached to a shaft. As the wind pushes the sails, the shaft is rotated which can then be used for mechanical power. One common use was to grind grain into flour. The Dutch refined windmill technology in the Middle Ages and built many windmills for agricultural processing.
Windmills were also used for pumping water. By attaching a pump to the rotating shaft, windmills could draw water up from underground wells or rivers to irrigate crops and provide drinking water. Wind-powered water pumps helped populate arid regions by providing a reliable water source.
Today, we primarily use wind to generate electricity. Wind turbines operate on the same principle as windmills, but instead of directly grinding grain or pumping water, they convert the rotational energy into electricity using a generator. Wind farms with dozens or hundreds of turbines now provide clean renewable energy around the world.
Ventilation
Wind plays a vital role in ventilating indoor and outdoor spaces by bringing in fresh air and removing pollutants. It works to circulate the air, replacing stale, dirty air with new, clean air. This refresh of oxygen helps create healthier environments for people, animals, and plants.
Inside our homes and buildings, open windows allow breezes to blow through, exchanging the air. Vents and fans also harness wind power to pull fresh air in and force old air out. This circulation removes hazardous fumes from paint, cleaning products, or gases and brings in clean oxygen. Proper ventilation with fresh air has been shown to improve cognitive function, health, and comfort indoors.
Outside, wind disperses and dilutes dangerous emissions from cars, factories, and other pollution sources. It blows these contaminants away from concentrated areas, helping clear the air of impurities. Gardens and trees also benefit from wind bringing fresh carbon dioxide and removing ethylene gas that can inhibit plant growth. Overall, the movement of air from wind is essential for sustaining clean, breathable air in our indoor and outdoor environments.
Seed dispersal
One of the most important ways that wind helps life on Earth is by dispersing seeds. As seeds develop on plants, many are designed to catch the wind. The wind then carries these seeds far away from the parent plant, spreading them over a wider area. This seed dispersal by wind allows plants to propagate and expand their ranges. It also prevents overcrowding and competition near the parent plant.
Plants like dandelions have light, feathery seeds that can float on the gentlest breeze. Maple trees and ash trees have winged seeds that almost seem to fly through the air. Even heavier nuts and acorns benefit from wind dispersal. While not carried as far, squirrels and other animals often knock these seeds from the trees to be scattered by wind. Without the helpful flow of air currents, many important plant species would not be able to reproduce and spread as effectively.
Weather and Climate
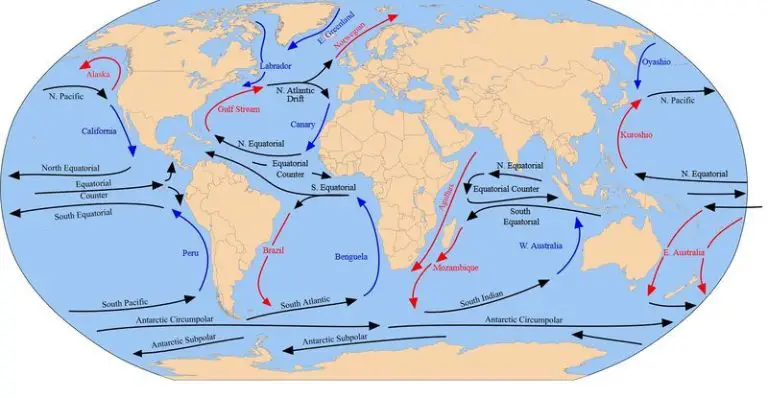
Wind plays a crucial role in influencing weather patterns and driving ocean currents that impact climate across the globe. As air moves due to differences in atmospheric pressure, it transports heat and moisture around the planet. This movement of wind drives ocean currents, which distribute heat and regulate global temperatures. Wind patterns also steer storm systems and moisture, affecting regional weather and precipitation. Changes in wind patterns and ocean currents can cause shifts in climate over months, years, or decades. Overall, wind serves as a key driver of dynamic weather and a moderating influence on climate through its continual circulation in the atmosphere and oceans.
Surface winds and upper atmosphere winds like the jet stream direct storm tracks and influence the path of weather systems. The convergence of winds can spark storm development while divergence breaks storms apart. Winds enable weather systems to shift across continents and oceans. In the tropics, winds converge to fuel thunderstorms that empty tremendous rains. At higher latitudes, cold polar winds clash with warmer air to generate extratropical cyclones that bring precipitation farther poleward. These and other wind patterns shape regional weather regimes around the world.
In the oceans, winds drive surface currents and upwelling that transports heat around the planet. The winds of the Trade Winds belt in the tropics push warm water westward. As this water meets continents, it deflects poleward to become currents like the Gulf Stream, transporting heat toward the poles and moderating climate in temperate regions. Changes in wind strength can impact the pace of these currents, altering how rapidly heat is redistributed. Upwelling winds along coasts pull up cold deep water, fueling fisheries. Overall, the global circulations driven by wind transfer enormous amounts of heat and help regulate Earth’s climate.
Changes in wind patterns due to climate variability and change can shift storm tracks, alter ocean circulations, and cause regional climate impacts. Studying the role of winds in weather and climate helps scientists understand our atmosphere and project future climate impacts. Overall, the invisible movements of air as wind provide a powerful shaper of weather and climate across the planet.
Recreation
Wind can provide enjoyment and recreation through outdoor activities like flying kites, windsurfing, and hot air ballooning. The force and flow of wind enables these activities that people do for fun and adventure.
Flying kites is a popular pastime around the world that relies on wind. When wind catches and lifts the kite, the kite soars up into the air. This allows the kite flyer to maneuver and control the kite as it dances and dips through the sky. Many kite flying festivals and competitions are held annually to showcase amazing kite skills and designs.
Windsurfing, also known as sailboarding, harness the power of the wind for an exciting surface water sport. Windsurfers stand on a board and control a large sail connected to the board. The wind propels the board across the water similar to how it propels a sailboat. Windsurfing allows fast rides across bays, lakes, and oceans for thrilling recreational enjoyment.
Hot air balloons also utilize the movement of wind for recreational flying. As hot air is pumped into the balloon, the balloon inflates and is carried into the air by the wind. The changing wind currents give hot air balloon rides an adventurous feel as the wind determines the direction and speed of flight. Hot air balloon festivals often occur because they provide a visually stunning form of recreation.
Conclusion
In summary, wind provides numerous helpful impacts in our daily lives. From generating renewable electricity to cooling effects on hot days, wind offers many benefits. Wind energy continues to grow as an essential source of power that doesn’t emit greenhouse gases. Wind propulsion enabled trade and exploration via sailing ships throughout history. The movement of air currents drives global weather and climate patterns that shape the world around us. On a more local level, wind provides ventilation to freshen indoor air. Seeds get dispersed over long distances thanks to the wind, helping vegetation spread. Wind makes enjoyable recreational activities like kite-flying and windsurfing possible. Clearly, wind plays an integral role in the planet’s ecosystems and in human societies. By understanding all the ways wind helps us, we can appreciate its importance and work to harness it as a sustainable resource.