How Do We Use Biomass In Everyday Life?
Biomass refers to organic material that comes from plants and animals. It is a renewable energy source that can be used for a variety of everyday purposes. Biomass contains stored energy from the sun, and it exists in the form of living or recently living plants and biological waste products.
Some of the most common uses of biomass in everyday life include fuel, energy, construction, paper products, textiles, packaging, hygiene, cosmetics, food, and gardening. This renewable resource helps provide us with the basic materials we depend on in our homes, workplaces, and communities.
In this article, we will take a closer look at how we utilize biomass in our day-to-day lives across these key areas. Examining the diverse ways biomass impacts and improves modern living provides a greater appreciation for this vital renewable resource.
Fuel and Energy
Wood and biomass can provide useful energy for heating, electricity, and transportation. Wood has been used as a classic form of fuel for heating and cooking for centuries. Burning wood for fuel releases the stored solar energy used by trees to grow. The combustion of wood produces heat that can be used for domestic heating, industrial processes, or electricity generation.
Wood pellets made from compacted sawdust or other wastes from the timber industry now provide a more concentrated and convenient form of woody biomass for heating and power. Wood pellets have the advantage of consistent quality and energy content. Their high density also makes transport over long distances more feasible.
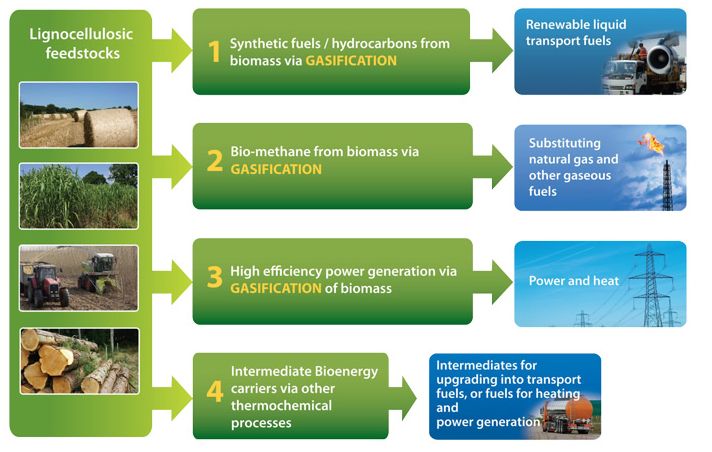
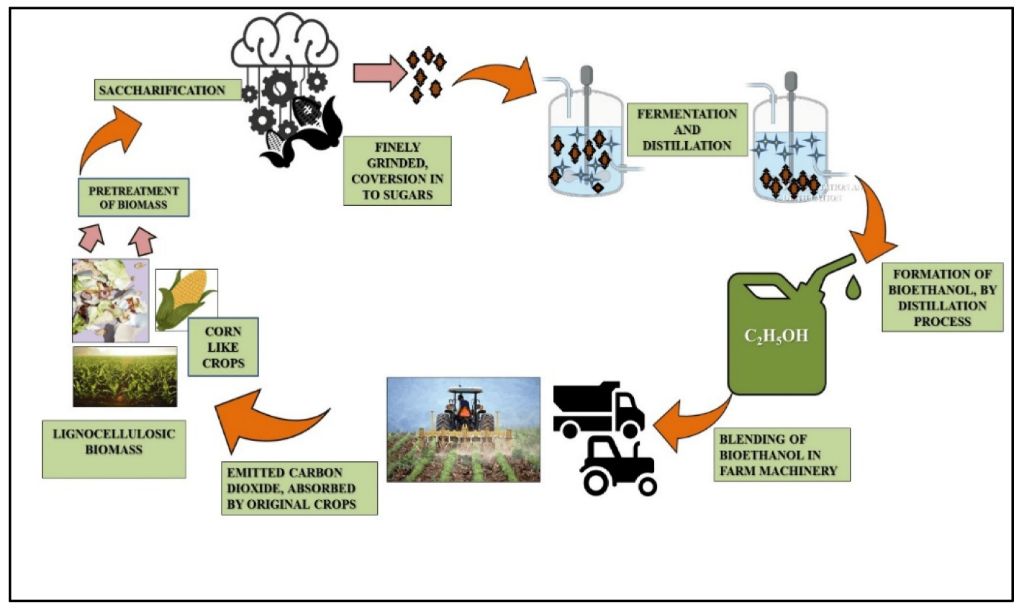
In addition to direct burning of woody biomass, wood can be converted into biofuels through processes like pyrolysis and gasification. These methods can produce renewable transportation fuels like bio-oil and biogas.
Ethanol produced from the fermentation of plant sugars is another important biofuel. Corn and sugarcane are common feedstocks, but cellulosic ethanol can also be produced from non-food plant sources like crop residues or woody biomass. Ethanol is widely blended with gasoline as a renewable transport fuel.
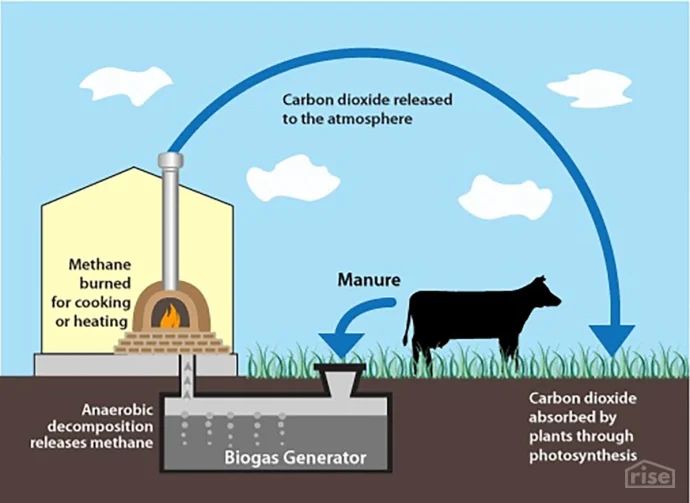
Biogas produced from anaerobic digestion of organic wastes like manure or crop residues is another versatile form of bioenergy. Biogas can provide heat, electricity, and even vehicle fuel after an upgrading process.
Using biomass energy from wood, biofuels, and biogas can reduce dependence on fossil fuels and lower net carbon emissions when sustainably produced. Bioenergy has the potential to provide substantial renewable power and heat across many sectors.
Buildings and Construction
Biomass is an integral material used in buildings and construction. The most common application is lumber from trees. Lumber is used for everything from framing and load-bearing elements to flooring, siding, doors, window frames, and furniture.
Wood’s high strength-to-weight ratio makes it an ideal construction material. It’s renewable, widely available, easy to work with, and aesthetically pleasing. Using lumber sourced from responsibly managed forests ensures a sustainable supply.
Engineered wood products like plywood, oriented strand board, and glulam beams take advantage of composite materials made by binding together wood strands, fibers, or veneers with adhesives. This makes efficient use of smaller wood pieces and results in strong, stable, standardized building materials.
Wood pulp or fiber is also used to make insulation, soundproofing materials, and medium-density fiberboard which is an engineered wood product used for cabinetry, furniture, flooring, and more.
Using biomass products like lumber minimizes the carbon footprint of construction by avoiding emission-heavy materials like steel, concrete, bricks, and plastics.
Paper and Cardboard
Paper and cardboard products are some of the most common items made from biomass. The raw material for paper production comes primarily from wood pulp and agricultural residuals like straw and bagasse. The pulp is processed, bleached, and treated to produce a variety of paper products.
Paper is an essential part of modern life, used for printing, packaging, tissues, notebooks, and more. Recycled paper accounts for approximately 37% of the raw material for paper manufacturing. However, the majority still comes directly from trees and plants. With global paper consumption continuing to rise, biomass remains crucial for meeting demand in a renewable and sustainable way.
Cardboard packaging is also predominantly sourced from wood pulp and other plant fibers. Corrugated cardboard boxes, cardboard tubes, food cartons and more all begin as biomass. As with paper, recycling plays an important role, but biomass inputs are still needed. Cardboard and paper products are highly recyclable and biodegradable, making biomass an excellent renewable resource.
Clothing and Textiles
Biomass from plants like cotton, flax, and hemp have long been used to create fabrics for clothing and other textiles. Cotton is by far the most commonly used natural fiber and accounts for around one third of all fiber used for clothing globally. The cotton plant produces bolls containing fluffy fibers that can be spun into yarn and woven or knitted into fabrics. Cotton is valued for its softness, breathability, and absorption. Linen is made from the fibers of the flax plant stalk and is known for its strength, coolness, and luster. Linen was one of the earliest fabrics ever produced, dating back thousands of years. Hemp fiber derives from the stalk of the hemp plant and is naturally more durable than cotton. Hemp textiles tend to get softer over time while maintaining their shape. In addition to clothing, biomass fabrics are also commonly used for towels, bed sheets, table linens, and other home textiles.
Packaging
Bioplastics are becoming an increasingly popular biomaterial used for packaging and containers. The most common types of bioplastics used are:
- PLA (polylactic acid) – made from corn starch or sugarcane
- PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) – made by microorganisms
- Starch blends – thermoplastic starch blended with biodegradable polyesters
These bioplastics can be manufactured into various packaging formats like clamshell containers, bottles, wrappers, bags and boxes. They are biodegradable and compostable, helping to reduce plastic waste and dependence on fossil fuels. Some key advantages of bioplastics for packaging:
- Renewable and sustainable – made from plants and agricultural byproducts
- Biodegrade much faster than traditional plastics – break down in industrial composters
- Use less energy to produce than traditional plastics
- Generates less greenhouse gas emissions
- Can be indistinguishable from traditional plastic packaging
There are some challenges with bioplastic packaging like higher costs and difficulty maintaining integrity under certain conditions. But continued innovation and economies of scale are helping make them more competitive with conventional plastic packaging.
Hygiene and Cosmetics
Biomass is an integral component of many hygiene and cosmetic products we use every day. Plant oils and fats are commonly used to produce soaps, shampoos, lotions and other personal care items.
The oils extracted from seeds, nuts and fruits like coconut, palm, olive, cacao and shea contain fatty acids that can cleanse, moisturize and nourish skin and hair. They are used as natural surfactants in soaps and shampoos to create lather and wash away dirt and oils. Plant-derived oils are also excellent emollients, leaving skin smooth and soft.
Lotion, creams, balms and salves also rely on plant oils and butters like jojoba, aloe, cocoa butter and almond oil to hydrate and protect skin. The vitamins and antioxidants in these natural ingredients impart anti-aging and healing properties as well. Cosmetics like lip balm and makeup contain plant waxes and oils for texture, shine and fragrance.
Using biomass materials rather than synthetic ingredients makes these self-care products more sustainable and environmentally-friendly. The renewable nature of plants, as well as biodegradability, aredistinct advantages over petroleum-derived chemicals. With consumers increasingly conscious about natural, organic and green beauty choices, plant-based cosmetics and toiletries will continue to grow in popularity.
Food and Feed
Biomass is an integral part of our food supply for both humans and animals. Many of the plant and animal products that we consume originate from biomass:
-
Plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and legumes are forms of biomass that we eat. They contain energy from the sun that was converted into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
-
Livestock like cows, pigs, and chickens are fed biomass in the form of grains, hay, silage, and other fodder crops. Their meat, milk, eggs and other animal products are sources of biomass-derived energy for us.
-
Fish like salmon and tilapia consume algae and other aquatic biomass. Their flesh provides biomass energy when eaten.
-
Honey comes from bees collecting and regurgitating flower nectar – another form of biomass.
Without biomass, our food system would not be able to function. It provides the foundation for the energy and nutrition that flows through the food chain.
Gardening and Landscaping
Biomass materials like mulch, compost, and other plant soil amendments play an important role in gardening and landscaping. Mulch is often made from bark chips, wood debris, straw, and other plant materials. It helps retain soil moisture, regulates soil temperature, prevents weed growth, and improves the soil as it decomposes over time. Compost is decayed organic matter that is rich in nutrients and used to fertilize soil. It is created by combining plant-based materials like yard trimmings, food scraps, manure, and straw in the proper conditions to break down over weeks or months. Compost enriches and conditions soil while creating an environment beneficial to plants and soil organisms. Other plant-based soil amendments like peat moss, coco coir fiber, leaf mold, grass clippings, and cover crops are also used to increase soil fertility and tilt for gardening, landscaping, and farming.
Conclusion
Biomass is an important renewable resource that we use in many aspects of everyday life. As we have seen, biomass is utilized as a fuel and energy source, in construction and manufacturing, and in a wide variety of consumer products. From the cars we drive, to the homes we live in, to the food we eat, biomass plays a role.
One of the key benefits of biomass is its sustainability. Biomass materials are derived from living or recently living plant and animal sources, making them renewable. This means we can produce and replenish biomass on an ongoing basis, unlike finite fossil fuel resources. However, it is important that biomass sources are managed responsibly through strategies like replanting forests or utilizing waste that would otherwise end up in landfills. This ensures the sustainability of biomass as an everyday resource.
In summary, biomass has become an integral part of modern life. With responsible sourcing and management, biomass can continue to provide renewable, sustainable materials and energy for our everyday needs.