How Can We Make Renewable Energy At Home?
Renewable energy is derived from natural resources that replenish at a higher rate than they are consumed, such as sunlight, wind, tides, and geothermal heat (https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/what-is-renewable-energy). Using renewable energy sources at home can reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lower energy bills, and decrease your carbon footprint. As climate change becomes an increasingly urgent issue, transitioning to renewable energy is vital for building a more sustainable future. There are many practical and affordable ways homeowners can adopt renewables. Generating your own renewable electricity, heating water with the sun, and cooking with biofuels are all impactful steps. With the right knowledge and incentives, every home can contribute to the renewable energy transition.
Solar Panels
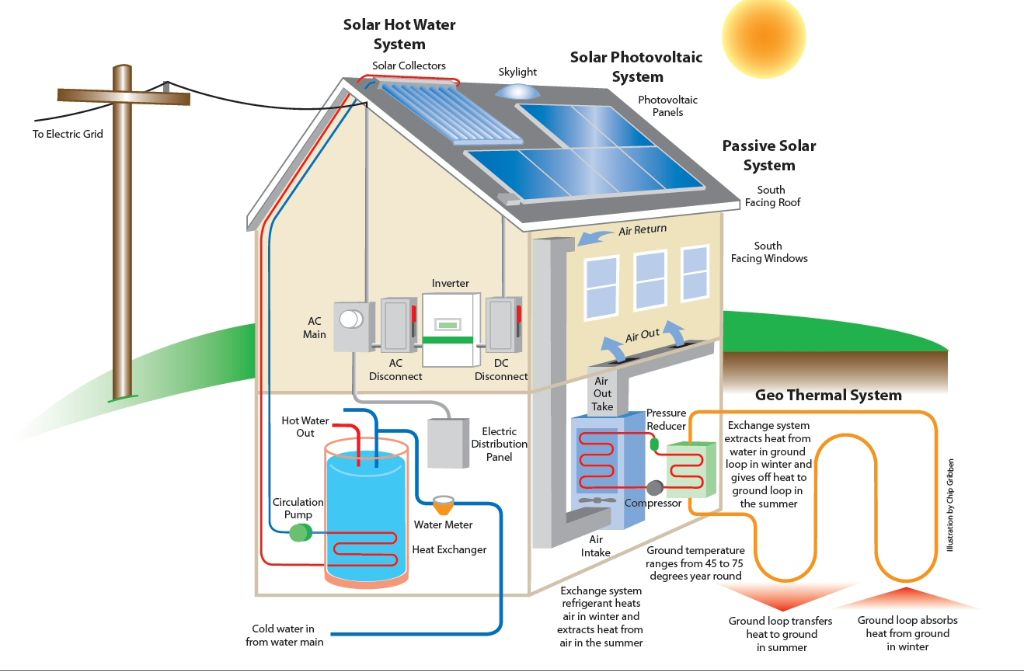
Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They work through the photovoltaic effect, whereby photons from sunlight knock electrons loose from atoms, generating a flow of electricity. Solar panels are made up of many individual solar cells that are connected together. The more light that hits the solar cells, the more electricity that is produced.
For residential use, solar panels are typically installed on the roof in an array, but they can also be mounted on the ground. The average home system size is around 6-8 kW and takes up about 400-600 square feet on the roof. According to recent estimates, solar panels cost between $18,000-$36,000 for an average-sized home system after tax credits and incentives (https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/finance/solar-panel-cost). The exact cost depends on system size, panel efficiency, location and local rebates/tax credits.
One of the benefits of solar panels is that they can generate electricity right at your home, reducing reliance on the grid. However, they do require unshaded space on your roof or land that gets daily sun. Solar only produces energy during daylight hours, so battery storage or net metering with the grid is needed to power your home around the clock.
Solar Water Heaters
Solar water heaters are a great way to use renewable energy at home to heat water. They use the power of the sun to heat water through solar thermal collectors placed on the roof. The solar thermal collectors contain tubes filled with water that heat up when the sun shines on them (https://www.construction21.org/articles/h/advantages-of-installing-a-solar-water-heater.html). The heated water is then stored in an insulated storage tank for use in the home.
There are two main types of solar water heating systems – active systems that circulate pumps to control water flow, and passive systems that rely on gravity and the tendency for water to naturally circulate as it heats. Passive systems are usually less expensive but active systems can be more efficient. Choosing the right system depends on climate, hot water usage, and budget.
The main benefits of solar water heaters are that they provide free hot water using renewable energy from the sun, reducing electricity bills. They also have environmental benefits by lowering greenhouse gas emissions from power plants. Solar water heating can provide around 50-80% of a household’s hot water needs (https://www.theleveredge.com/news/the-top-5-benefits-of-solar-water-heaters/). With the right climate and system, solar water heaters are a great way to utilize renewable energy at home.
Small Wind Turbines
Small wind turbines allow homeowners to harness wind energy on a small scale to help power their homes. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, small wind turbines for residential use typically range from 400 watts to 20 kilowatts in size. The turbines work by converting the kinetic energy of wind into rotational energy to run a generator that produces electricity.
To successfully implement small wind turbines at home, there are permitting and placement considerations. Many areas require permits, so homeowners will need to check local zoning laws and regulations. The turbines need to be sited in open areas with consistent wind at average speeds of at least 9 mph. Typically small wind turbines are mounted on towers or rooftops at least 30 feet high in order to access faster wind speeds at higher altitudes.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps use the constant temperatures underground to provide heating and cooling for homes and buildings. They take advantage of the fact that underground temperatures are warmer than air in winter and cooler in summer (Energy.gov).
Geothermal heat pumps circulate water or an anti-freeze solution through pipes buried underground, either vertically or in a loop. The fluid absorbs heat from the earth in winter, bringing it indoors to warm the air. The process is reversed in summer, pulling heat from indoors and depositing it into the cooler earth (RMI).
Compared to conventional heating and cooling systems, geothermal heat pumps use 70-80% less electricity. They take advantage of free heating and cooling energy from the earth’s constant subsurface temperatures (Energy.gov). This makes them a clean, renewable way to achieve heating and cooling for a home.
Microhydropower
Microhydropower describes generating electricity from small, low-impact water systems. Microhydro systems capture the kinetic energy of flowing water and use it to turn a turbine connected to a generator (Energy.gov, 2023). These systems can be installed on properties with access to moving water, such as a stream, river, or even canal. The flowing water passes through the turbine causing it to spin, which then activates an alternator to generate electricity.
Microhydro setups do not require large dams or infrastructure projects, making them suitable for homes, farms, or small businesses. They provide a reliable, renewable energy source without major environmental impacts. A typical microhydro system can generate up to 100 kW of electricity, providing a sustainable power supply for off-grid homes or supplementing the main grid (Buildwithrise.com, 2020). With proper planning and installation, microhydropower can be an accessible and underutilized form of clean, renewable energy generation at the residential level.
Biofuel Generators
Biofuel generators allow homeowners to produce their own fuel and power their generators with renewable biofuels like biodiesel or ethanol. Biodiesel can be made from vegetable oils or animal fats, while ethanol is made from fermenting plant sugars. Running generators on biofuels has several advantages:
Biofuels are renewable and can be produced at home, providing energy independence and security. The raw materials like used cooking oil or corn can be sourced locally. Biodiesel emits less air pollutants than diesel, reducing the generator’s environmental impact (Source).
Biofuel generators can run on 100% biodiesel or ethanol, or on a blend with conventional diesel or gasoline. Many dual-fuel generators are compatible with B20 biodiesel blends. Converting a diesel generator to operate on biodiesel may require minor modifications like changing seals to biodiesel-compatible materials.
While the energy density of biofuels is a bit lower than conventional fuels, they remain quite practical for running generators. Homeowners with ready access to feedstocks like used cooking oil can potentially produce their own fuel at low cost. However, biofuel production does require time, effort and some investment in equipment.
Energy Efficient Appliances
Making simple upgrades to your home appliances and electronics can help reduce your energy usage and save you money on utility bills. Here are some tips for using less energy for cooking, cooling, cleaning and entertainment at home:
Cooktops & Ovens – When it’s time to replace your stove, choose an energy efficient model with induction or natural gas cooktops. Make sure it has an Energy Star rating. Use lids on pots and pans to retain heat. Match the size of the pan to the burner. Turn off cooking appliances a few minutes before cooking time ends.
Refrigerators – Look for Energy Star certified models which use at least 15% less energy than standard models. Make sure to regularly clean coils and seals and don’t keep the refrigerator too cold. Only open the door when necessary and don’t leave it open too long.
Dishwashers – Scrape food scraps off dishes instead of rinsing them before loading. Run full loads and use the energy-saver setting. Allow dishes to air dry. Clean the filter monthly.
Washing Machines – Wash with cold water instead of hot. Clean lint filter after each load. Run full loads but don’t overload. Let clothes air dry when possible.
Lights – Switch to energy efficient LED lighting. Turn off lights when not needed. Use natural light when possible. Use dimmers, motion sensors, and timers.
Passive Solar Home Design
Passive solar home design takes advantage of the sun’s energy through strategic building orientation and placement of windows, overhangs, and thermal mass (https://www.energy.gov/energysaver/passive-solar-homes). The goal is to maximize solar heating and lighting without the use of mechanical systems or devices.
Key elements of passive solar design include:
- Orienting the house to face within 30 degrees of due south to maximize solar gain
- Installing large, high performance windows on the south side to let in sunlight and heat
- Using thermal mass like concrete floors or tiles to absorb and slowly release heat
- Adding overhangs above south facing windows to block high summer sun
- Using strategies like light shelves to bounce sunlight deeper into a home
- Planting deciduous trees on the south and west sides for shading in summer and solar access in winter
Benefits of passive solar design include free heating and lighting, improved comfort, and lower energy bills. However, passive solar homes require careful design based on climate and solar orientation (https://home.howstuffworks.com/home-improvement/construction/green/10-benefits-of-a-passive-house.htm). When done right, passive solar design can eliminate or drastically reduce the need for heating and lighting systems.
Conclusion
In summary, there are many ways that homeowners can generate renewable energy right at home. Installing solar panels, solar water heaters, small wind turbines, geothermal heat pumps, microhydropower systems, and biofuel generators can all help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and transition to cleaner energy sources. With dropping costs and improving technologies, renewable energy systems for the home will likely continue growing in popularity into the future.
Generating your own renewable electricity and heat can save money on utility bills, increase home value, and reduce your carbon footprint. While upfront costs can be high, many systems offer rapid payback periods and government incentives are often available. With careful planning and research, renewable energy systems can be an accessible and smart investment for eco-conscious homeowners looking to do their part in fighting climate change.
Transitioning our energy infrastructure worldwide from fossil fuels to renewables is critical in the fight against climate change. But this enormous task starts at the individual level, with everyday people embracing changes like generating their own renewable energy at home. The future will rely on these small steps that add up to big change.