How Can Renewable Energy Generate Electricity?
Renewable energy comes from naturally replenishing sources and is increasingly important for electricity generation worldwide. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy sources are clean and sustainable. Some key renewable energy sources used for electricity generation include solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, bioenergy, and wave/tidal power.
Generating electricity from renewable sources has many benefits compared to fossil fuels. Renewables produce no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, reducing air pollution and mitigating climate change. They also enhance energy security by relying on domestic resources rather than imported fossil fuels subject to price volatility. This content will provide an overview of how some of the main renewable technologies can generate electricity to meet society’s needs in a sustainable manner.
Solar Power
Solar power generates electricity from sunlight using the photovoltaic effect. Solar panels contain photovoltaic cells made of materials like silicon that absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons. The flow of these electrons generates an electric current that can be used as electricity. The more sunlight that hits the solar panels, the more electricity they can produce.
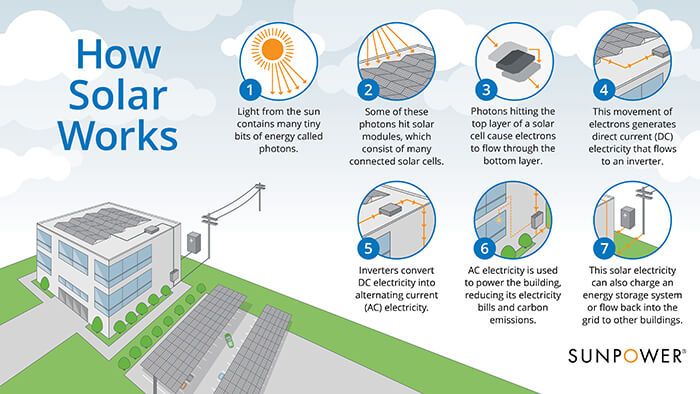
Another approach is solar thermal electricity generation, where sunlight is concentrated by mirrors or lenses to heat up a fluid that produces steam to spin a turbine and generator. This allows solar thermal plants to store the heat and produce electricity even when the sun isn’t shining.
Some of the largest solar power plants in the world include Bhadla Solar Park in India, which covers over 10,000 acres and has a capacity of 2,245 MW. The Benban Solar Park in Egypt has a capacity of 1,650 MW spread over 37 solar power plants. In the United States, Solar Star is one of the biggest at 579 MW capacity.
Wind Power
Wind turbines harness the natural power of wind to generate electricity. As wind blows over the blades of the turbine, the kinetic energy of the wind causes the blades to spin. This spinning motion turns a shaft inside the turbine, which connects to a generator and produces electricity (1).
Most wind turbines are installed on land in groups called wind farms, also known as onshore wind. Some of the largest onshore wind farms are located in China, such as the Gansu Wind Farm with over 7,000 turbines (2). The United States also has many large-scale onshore wind projects like the Roscoe Wind Farm in Texas with 627 turbines and a capacity of 782 megawatts (3).
Offshore wind farms are installed in bodies of water, usually oceans or large lakes. Offshore wind power holds great potential, especially in Europe, with steadier and stronger winds compared to onshore. The Hornsea Project One in the North Sea off the UK coast is the world’s largest offshore wind farm, with 174 turbines generating 1,218 megawatts of power (4). Other major offshore wind projects are coming online globally, like the Formosa 1 project off Taiwan and Vineyard Wind 1 off Massachusetts in the United States (5).
Wind power comprised over 14% of total installed power generation capacity in Europe in 2021 and continues to expand its share of clean electricity generation worldwide (6). With larger turbines and farms coming online, wind power production is projected to grow steadily in the coming decades.
Sources:
(1) https://www.energy.gov/eere/wind/how-do-wind-turbines-work
(2) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gansu_Wind_Farm
(3) https://www.power-technology.com/projects/roscoe-wind-farm/
(4) https://hornseaprojectone.co.uk/
(5) https://www.offshorewind.biz/2021/08/13/formosa-1-offshore-wind-farm-officially-commissioned/
(6) https://windeurope.org/intelligence-platform/product/wind-energy-in-europe-2021-statistics-and-the-outlook-for-2022-2026/
Hydropower
Hydropower generates electricity by using the energy from flowing water to spin turbines connected to generators. The moving water spins the turbine blades, which rotates a shaft connected to the generator, producing electricity. There are two main types of hydropower systems:
– Run-of-river – Divert a portion of a river’s water through a canal or penstock to spin turbines. The water is returned to the river downstream.
– Reservoir – Stores water behind a dam on a river. The dam controls water flow through turbines to generate electricity as needed.
Some of the largest hydropower dams in the world include:[1]
- Three Gorges Dam in China – 22,500 MW capacity[2]
- Baihetan Dam in China – 16,000 MW capacity
- Guri Dam in Venezuela – 10,200 MW capacity
Hydropower provides renewable electricity with minimal greenhouse gas emissions. However, large dams can impact river ecosystems and displace communities. Overall, hydropower remains a major source of renewable energy globally.
Geothermal
Geothermal power plants use heat from under the earth’s surface to produce steam to spin turbines for electricity generation. There are three main types of geothermal power plants:
– Flash steam plants use steam from reservoirs close to the earth’s surface. The steam goes directly through pipes to spin the turbine generators. Major flash steam plants include The Geysers in California and Wairakei in New Zealand.ThinkGeoEnergy’s Top 10 Geothermal Countries 2022
– Binary cycle plants transfer hot water from deeper reservoirs to heat a secondary fluid with a lower boiling point. This causes the secondary fluid to flash to vapor and spin the turbines. Major binary cycle plants include Heber and Salton Sea in California.
– Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) inject water into hot dry rocks deep underground at high pressures. The injected water captures the heat of the rocks and returns to the surface as hot water or steam to power turbines. EGS has potential for major growth but currently faces technical challenges.
Indonesia, the Philippines, and the United States lead geothermal power generation globally. In 2021, the top five countries for geothermal capacity were the U.S. (3,677 MW), Indonesia (2,435 MW), the Philippines (1,916 MW), Turkey (1,500 MW), and New Zealand (1,005 MW).Top Five Geothermal Power Generation Markets in 2021
Bioenergy
Bioenergy involves burning organic matter like plants and waste to generate electricity. Biomass contains stored energy from sunlight which can be released through combustion. Global electricity production from biomass was 685 TWh in 2020.
Biomass can be burned directly to produce heat that boils water to spin turbines connected to generators. Common biomass fuels include wood, agricultural waste, and methane from landfills or wastewater treatment. Crops like miscanthus and switchgrass can also be grown specifically for energy production.
Some examples of biomass power plants include the Drax Power Station in the UK which burns wood pellets, and the Huozhong Agricultural and Sideline Products Biomass Power Generation project in China which uses crop residues. Converting biomass to energy can reduce waste and provide carbon-neutral renewable electricity.
Wave & Tidal
Wave and tidal energy systems harness the kinetic energy of ocean waves and tides to generate electricity. As waves travel across the surface of the ocean, they contain kinetic energy that can be captured by wave energy converters and converted into electricity. Similarly, the rise and fall of tides contain kinetic energy that can be tapped by tidal power plants. There are several emerging technologies to capture this energy:
Wave energy converters like point absorbers use buoys to convert the up-and-down motion of waves into mechanical energy, which is then turned into electrical energy. Oscillating water column devices use waves to compress air in a chamber, powering an air turbine. Overtopping devices have reservoirs that waves can fill up, then drain through turbines. Examples of pilot wave energy projects include the Mutriku Wave Energy Plant in Spain and the Carnegie Clean Energy project in Australia (Source).
Tidal energy technologies include tidal stream generators, which use underwater turbines spun by tidal currents, similar to wind turbines. Tidal barrages build dams across tidal estuaries, controlling the flow of huge volumes of water that drive turbines. Examples include the Sihwa Lake Tidal Power Station in South Korea and the La Rance Tidal Power Plant in France, the world’s first major tidal power station (Source).
Wave and tidal energy have the potential to provide renewable, low-carbon electricity to coastal communities worldwide. However, technology costs, infrastructure needs, and environmental impacts remain challenges to wider adoption.
Other Technologies
In addition to the major renewable electricity sources like solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and bioenergy, there are some emerging technologies that show promise for electricity generation in the future. One example is hydrogen fuel cells, which produce electricity through an electrochemical reaction using hydrogen fuel and oxygen from the air. Fuel cells are attractive because they can produce electricity without combustion or emissions. While hydrogen fuel cells currently have some cost and scaling challenges, they have potential for applications like powering electric vehicles and providing electricity in remote locations [1]. Other emerging renewable technologies include ocean wave and tidal power, which harness energy from waves or tidal currents. These are still in early stages, but could one day provide renewable electricity to coastal areas. [2]
Environmental Benefits
Renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, hydropower, geothermal, bioenergy and ocean power generate electricity with significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel sources like coal, oil and natural gas. According to the UN, renewable energy could provide 65% of the world’s electricity and reduce power sector emissions by 90% by 2030 (source).
When renewable sources generate electricity, they produce little to no global warming emissions. In contrast, fossil fuel plants contribute significant amounts of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide that trap heat and warm the planet. The US Energy Information Administration found that in 2019, renewable sources produced 11% of U.S. energy but only 7% of energy-related CO2 emissions. Expanding renewables can drastically cut emissions from power generation.
Beyond climate benefits, renewable energy results in cleaner air by reducing smog-forming pollutants emitted by fossil fuel plants. This improves public health by decreasing respiratory and cardiovascular problems. The Union of Concerned Scientists estimates renewable energy could prevent over 35,000 premature deaths in the U.S. by 2050 (source). The transition to carbon-free renewables is critical to curb the impacts of climate change and build a sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
Renewable energy offers a vital way for the world to generate electricity while reducing dependence on fossil fuels. There are many mature technologies like solar, wind, hydropower and geothermal that can provide clean renewable electricity at scale today. Other emerging technologies like wave, tidal and bioenergy offer additional potential. By transitioning electricity generation to renewables, we can greatly reduce air and water pollution while mitigating climate change. Renewable energy also provides energy security by using inexhaustible domestic resources rather than imported fossil fuels. For these reasons, it is imperative that societies continue to develop renewable electricity and make the full transition away from coal and natural gas power as soon as possible.
In summary, there are many viable and scalable ways renewable energy can generate the electricity the world needs. Solar, wind, water and geothermal resources can all be harnessed with today’s technologies while newer options like ocean energy continue to develop. The environmental and economic advantages of renewable electricity make it vital that we rapidly transition from fossil fuel power generation. With the right investments, policies and commitment, renewable energy can fully supply the world’s electricity sustainably and securely.