Environmental Impacts Of Geothermal Energy
The Earth holds an immense store of hidden heat just beneath our feet. Miles below the surface, heat from the planet’s interior continues to slowly seep upward, warming the ground itself. This natural reservoir of thermal energy has long been recognized as a potential renewable energy resource for humanity. Geothermal energy harnesses the Earth’s internal heat for various applications such as generating electricity, providing heating and cooling to buildings, and more. While geothermal power holds promise as a clean and reliable energy source, its development and use also presents environmental challenges that must be addressed. In this post, I will explore both the benefits and drawbacks of geothermal energy from an environmental perspective, examining its impacts and how any issues might be mitigated. We will see that geothermal, like any technology, is not without tradeoffs that deserve careful consideration as nations strive to transition to renewable and sustainable energy systems.
Introduction To Geothermal Energy And Its Benefits For The Environment
Geothermal energy is a clean and sustainable source of energy that is harnessed from the Earth’s internal heat. It offers numerous benefits to the environment, making it an attractive alternative to traditional fossil fuels. One of the primary benefits of geothermal energy is that it produces no greenhouse gas emissions, making it a cleaner, more environmentally friendly option for power generation.
In addition to being emission-free, geothermal energy also has a low environmental footprint compared to other forms of energy. Unlike traditional energy sources that require extensive mining, drilling, and transportation of materials, geothermal energy requires only a small surface area for the installation of a geothermal power plant. Moreover, the installation of underground geothermal systems does not negatively impact animal habitats, soil quality, or groundwater supplies.
Another significant environmental benefit of geothermal energy is its ability to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. The transition to renewable energy sources like geothermal energy can play an essential role in mitigating the consequences of climate change by diminishing the amount of carbon emissions into the atmosphere.
Geothermal energy also offers economic benefits to local communities by reducing reliance on imported fuels and creating job opportunities in rural areas where geothermal resources are often located. The reduced dependence on fossil fuels ensures a more stable and predictable energy supply, which translates to more secure and sustainable local economies.
How Geothermal Energy Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Geothermal energy is an attractive alternative to traditional fossil fuels due to its ability to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The production of electricity from geothermal sources emits less than 1% of the carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions produced by coal-fired power plants. This remarkable difference is due to the fact that geothermal energy uses the Earth’s natural heat to generate electricity, without burning fossil fuels.
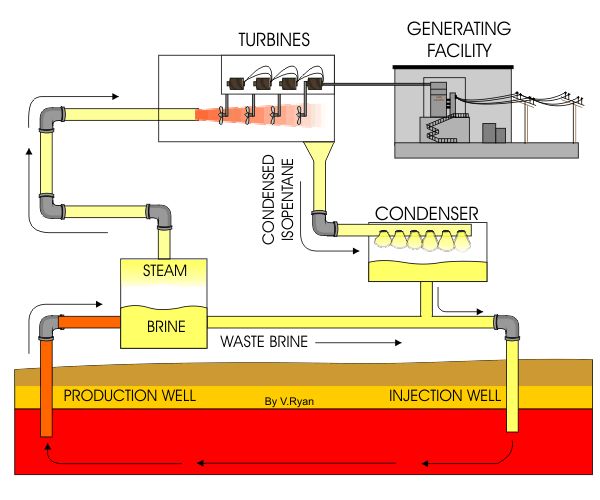
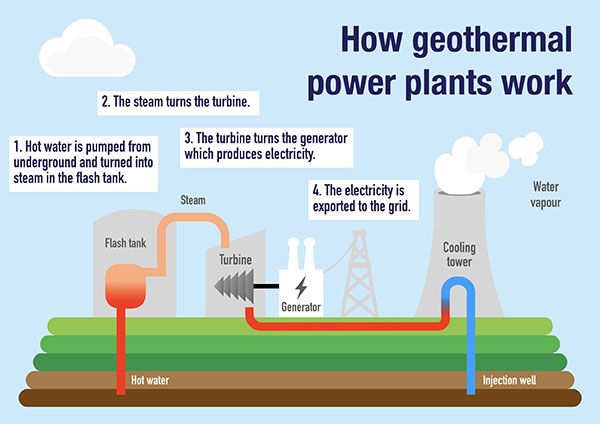
The process of geothermal power generation involves the extraction of hot water or steam from deep beneath the Earth’s surface. This hot water or steam is then used to drive turbines that generate electricity. Once the energy is harnessed, the cooled water or steam is returned to the geothermal reservoir, where it is reheated and the cycle begins anew. This process does not release any significant amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, making it a much cleaner and more sustainable source of energy.
By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, geothermal energy makes a significant contribution to mitigating climate change. The transition to renewable energy sources like geothermal energy can help to halt the continued increase in atmospheric greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). This is critical in light of the fact that global greenhouse gas emissions have reached unprecedented levels over the past few decades and are causing significant environmental damage.
The Role Of Geothermal In Mitigating Climate Change
The role of geothermal energy in mitigating climate change cannot be understated. As one of the few renewable energy sources that can provide both baseload power and heating, geothermal energy has the potential to significantly reduce global greenhouse gas emissions. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), geothermal energy has the potential to supply up to 3.5% of the world’s electricity needs by 2050, while simultaneously reducing CO2 emissions by more than 1.2 billion tonnes per year.
Moreover, geothermal energy can play a crucial role in the decarbonization of other sectors, such as industry and transportation. The direct use of geothermal energy for district heating and cooling, for example, can replace the burning of fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Similarly, the use of electric vehicles powered by geothermal electricity can help to decarbonize the transportation sector.
Beyond reducing greenhouse gas emissions, geothermal energy also offers numerous other environmental benefits. For example, unlike fossil fuels, geothermal energy does not produce air pollution or toxic waste, making it a much cleaner and healthier energy source. Geothermal power plants also require minimal land use compared to other types of power plants, as they can be built in areas where the ground is already disturbed, such as near oil and gas wells or abandoned mines.
However, like any energy source, geothermal energy also presents environmental challenges that must be addressed. For example, the drilling of geothermal wells can cause seismic activity, and the disposal of used geothermal fluids can lead to environmental contamination. Nevertheless, with careful planning and management, these environmental impacts can be minimized and the benefits of geothermal energy can be fully realized.
Case Studies Showcasing Successful Geothermal Projects Around The World
1. Hellisheidi Power Plant, Iceland
The Hellisheidi Power Plant in Iceland is the largest geothermal power plant in the world, producing 303 MW of electricity and 133 MW of thermal energy. The plant has been in operation since 2006 and has played a critical role in Iceland’s transition away from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. By using the geothermal resource available under the nearby Hengill volcano, the plant is able to provide electricity and heating to over 60,000 homes in the surrounding area, reducing the country’s greenhouse gas emissions by an estimated 185,000 tonnes per year.
In addition to providing energy, the Hellisheidi Power Plant has also helped support important research into the use of geothermal energy for carbon capture and storage (CCS), a process that can remove carbon dioxide emissions from power plants and industrial processes and store it underground. The Hellisheidi Power Plant is one of the few geothermal power plants in the world that has successfully integrated CCS technology into its operations, making it a key example of the potential for geothermal energy to not only reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but also actively remove them from the atmosphere.
2. Olkaria Geothermal Power Plant, Kenya
The Olkaria Geothermal Power Plant in Kenya is another successful example of the use of geothermal energy to provide electricity to communities in need. Located in the Great Rift Valley in central Kenya, the plant harnesses the region’s geothermal resources to provide power to over 1 million homes across the country. The plant currently has a capacity of 825 MW, making it the largest geothermal power plant in Africa, and has helped to reduce Kenya’s reliance on imported fossil fuels.
One of the key benefits of the Olkaria plant is its ability to provide reliable and affordable electricity to people living in remote and rural areas of Kenya. Prior to the development of the plant, many communities in these areas did not have access to electricity and relied on small-scale, diesel-powered generators for their energy needs. The Olkaria plant has helped to change that, providing a stable and sustainable source of electricity and spurring economic growth across the region.
3. Larderello Geothermal Field, Italy
The Larderello Geothermal Field in Tuscany, Italy, has a long and storied history as one of the world’s first commercial geothermal power plants. The field was first discovered in the early 1900s, and by the 1920s, it was already producing electricity from geothermal sources.
Today, the Larderello Field remains a critical component of Italy’s energy infrastructure, producing over 600 MW of electricity and providing heating to communities across the region. The field is also home to some of the most innovative research in the geothermal energy sector, with scientists and engineers exploring new methods of extracting geothermal heat from deep below the earth’s surface.
Perhaps one of the most interesting aspects of the Larderello Field is the way it has been integrated into the local landscape. The region’s hot springs and geothermal pools have long been a popular tourist destination, and the development of the geothermal field has helped to further this industry. Visitors to the area can learn about the history of geothermal energy while enjoying the natural beauty and relaxation of the region’s thermal baths.
Challenges And Limitations Of Widespread Adoption Of Geothermal Energy
Despite the many benefits and success stories of geothermal energy, it is not without its challenges and limitations, which must be considered in the widespread adoption of this renewable energy source.
One of the biggest challenges of geothermal energy is the limited availability of suitable geothermal resources. In order to generate electricity from geothermal sources, it is necessary to have access to hot water or steam reservoirs deep beneath the Earth’s surface. These reservoirs are not evenly distributed around the world, and in many regions, the available resources may not be sufficient to support large-scale geothermal power generation. In addition, the exploration and development of geothermal resources can be costly and time-consuming, requiring significant investment and technical expertise.
Another notable limitation of geothermal energy is its potential impact on land use and natural habitats. Geothermal power plants require significant amounts of land to accommodate their infrastructure, including wells, pipelines, and transmission lines. This land use can have negative effects on local ecosystems and biodiversity, as well as potentially displacing human communities and disrupting traditional land use practices. Additionally, the drilling and injection of fluids associated with geothermal power generation can potentially trigger earthquakes or other seismic activity, further exacerbating environmental impacts.
Moreover, another limitation of geothermal energy is the variability of geothermal resources. Unlike other renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, geothermal energy is not consistent throughout the day or year. This variability can reduce the reliability of geothermal power plants as a consistent source of energy. Additionally, geothermal energy is subject to the same limitations as other renewable energy sources, such as the need to integrate with existing energy infrastructure and the potential for regional disparities in resource availability and energy costs.
In spite of these challenges and limitations, geothermal energy remains a promising renewable energy source with significant potential for expanded use and development. Continued research and innovation in geothermal technology, as well as improvements in land use planning and community engagement, can help to mitigate the negative impacts of geothermal power development and address the challenges of widespread adoption. With careful consideration and responsible development, geothermal energy can play a valuable role in meeting the world’s energy needs while helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and supporting sustainable development.
Innovations And Advancements In Geothermal Technology For Better Environmental Outcomes
In recent years, there have been numerous advancements in geothermal technology aimed at reducing the negative environmental impacts associated with geothermal energy production. These innovations have focused on a variety of areas, from exploration and resource identification to drilling techniques and power plant design.
One area of innovation in geothermal technology is the use of low-temperature geothermal resources. In many regions, the available high-temperature resources may be limited, and accessing them can be expensive and environmentally challenging. However, low-temperature geothermal resources, which typically have water temperatures between 50°C and 150°C, are more widely available and often easier to access. To take advantage of these resources, new technologies have been developed that allow for efficient heat exchange with lower temperature water, enabling the production of electricity from previously untapped sources.
Another area of innovation in geothermal technology is the use of enhanced geothermal systems (EGS). EGS involves creating artificial geothermal reservoirs by fracturing rock formations and circulating water through them. This technique can greatly increase the availability of geothermal resources, as well as reduce the environmental impact of traditional geothermal drilling. EGS has the potential to expand the reach of geothermal energy to areas with limited natural resources, such as urban areas and regions with low geothermal gradients.
In addition to these innovations in resource identification and drilling techniques, advancements have also been made in geothermal power plant design. For example, some geothermal power plants have begun to use binary cycle technology, which involves using a secondary fluid, such as ammonia or a hydrocarbon, to transfer heat from the geothermal source to the power plant’s turbines. Binary cycle technology can reduce the environmental impact of geothermal power generation by reducing the amount of water that needs to be withdrawn from natural sources, as well as reducing the risk of groundwater contamination.
Furthermore, there have been efforts to develop geothermal power plants that minimize land and habitat impacts, such as compact modular designs that reduce the amount of land required for infrastructure. These designs can also reduce construction costs and improve the overall efficiency of geothermal power plants.
Finally, advancements in data analysis and modelling software are improving resource identification and exploration. These technologies can help to identify geothermal resources with greater accuracy and identify potential risks associated with drilling and resource utilization.
Comparison Of Geothermal Energy With Other Renewable Energy Sources
Geothermal energy is just one of the many renewable energy sources that we have at our disposal. Other sources include wind, solar, hydropower, tidal power, and biomass. Each of these sources has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, with some being more suitable for certain applications than others.
When compared to other renewable energy sources, geothermal has several distinct advantages. For one, geothermal sources are available regardless of the weather conditions, unlike wind and solar energy which can be intermittent. Additionally, geothermal energy can be utilized in a variety of applications, ranging from electricity generation to heating and cooling systems. This versatility makes geothermal energy a valuable resource for a variety of industries.
In terms of environmental impact, geothermal energy is generally considered to be one of the more sustainable and clean energy sources available. The process of extracting geothermal energy does not produce any greenhouse gas emissions, making it an ideal solution for reducing the carbon footprint of energy consumption. Furthermore, geothermal power plants typically have a small footprint and do not take up a significant amount of land, unlike hydropower plants or wind turbines.
That being said, geothermal energy is not entirely free of environmental impact. The drilling and exploration required to access geothermal sources can disrupt surrounding ecosystems and disturb local wildlife. Geothermal power plants also require a significant amount of water, which can put stress on local water resources if not properly managed. Additionally, geothermal energy is not as widely available as other renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, and is therefore not an ideal choice for all regions.
Ways Individuals Can Support And Advocate For Geothermal Energy Development
Geothermal energy has the potential to be a game-changer in the transition towards renewable energy systems. If you are an individual who cares about the environment and wants to support the development of sustainable and clean energy sources, there are a number of actions you can take to advocate for geothermal energy.
One of the most important ways to support geothermal energy is to educate yourself and others about its benefits and drawbacks. By spreading awareness about geothermal energy, you can help to increase public demand for its development and adoption. This can be achieved by sharing information about geothermal energy with your friends, family, and community members, as well as through social media and public events.
You can also support geothermal energy development by engaging with your local policymakers and advocating for policies and regulations that incentivize its use. This can include supporting tax incentives or subsidies for geothermal energy projects, working to streamline the permitting process for geothermal drilling and exploration, or advocating for increased funding for geothermal research and development.
Another way to support geothermal energy is to invest in geothermal energy companies or projects. By putting your money into these initiatives and demonstrating financial support for geothermal energy, you can help to accelerate its adoption and development. Additionally, supporting companies that prioritize environmentally sustainable practices can help to push the industry towards more responsible and eco-friendly approaches.
Finally, you can support geothermal energy by reducing your own energy consumption and promoting energy efficiency measures in your home and community. By conserving energy and reducing the demand for fossil fuels, you can help to reduce the need for environmentally damaging energy sources and make the case for cleaner alternatives such as geothermal energy.
Conclusion Highlighting The Potential Of Geothermal Energy To Combat Environmental Issues.
One of the key advantages of geothermal energy is its low carbon emissions profile. Unlike traditional fossil fuels, which release harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and contribute significantly to climate change, geothermal energy generates no carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases during operation. This makes it an ideal candidate for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change, which is one of the most pressing environmental issues facing our planet today.
Another benefit of geothermal energy is its reliability and consistency. Unlike other renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, geothermal energy is not dependent on weather patterns or other external factors. Instead, it relies on the natural heat reservoirs found deep within the Earth, which are constantly replenishing themselves. This means that geothermal energy can provide a steady and consistent source of power, without the variability that can sometimes be associated with other renewable energy sources.
Of course, as with any technology, there are also drawbacks and challenges associated with geothermal energy. These may include concerns around the environmental impacts of geothermal drilling and exploration, as well as potential risks to local ecosystems and communities. However, with careful planning, monitoring, and mitigation strategies, these challenges can be addressed, and the potential benefits of geothermal energy can be realized.
Ultimately, geothermal energy represents an important tool in our ongoing efforts to combat environmental issues and build a more sustainable future. By supporting geothermal energy development and adoption, we can reduce our reliance on finite and environmentally damaging fossil fuels, while harnessing the natural thermal energy available right beneath our feet. So let us all do our part to support geothermal energy and build a more sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that geothermal energy has significant benefits for the environment. From reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigating climate change, this renewable energy source has a crucial role to play in our fight against environmental issues. The case studies presented have shown us that successful geothermal projects are not just limited to one region or country, but can be implemented successfully around the world. However, it is important to acknowledge the challenges and limitations that still exist in adopting geothermal energy on a larger scale. Despite these obstacles, there have been exciting innovations and advancements in geothermal technology that offer hope for a more sustainable future.
We cannot deny the potential of geothermal energy in combatting environmental issues. Its ability to provide constant and reliable power makes it a valuable addition to our existing renewable energy sources. As we continue to see the damaging effects of climate change and the urgency for action, it is crucial for individuals to support and advocate for the development of geothermal energy. Whether through promoting policy changes or investing in renewable energy companies, every effort counts towards creating a cleaner and greener future.
Furthermore, as we compare geothermal energy with other renewable sources such as solar and wind power, we can see its unique advantages and potential synergies. As we strive towards a more sustainable future, it is essential to consider all available options and work together towards a common goal.
In conclusion, geothermal energy holds tremendous potential as an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels. It has already proven itself as a reliable source of clean energy and continues to evolve with innovations and advancements that make it even more promising. However, its widespread adoption is only possible through collective efforts from governments, businesses, and individuals. By embracing geothermal energy as part of our transition towards cleaner and greener solutions, we can make tangible progress in mitigating climate change and preserving our planet for future generations. Let us continue to support this remarkable form of renewable energy and build a brighter, sustainable future together.