Does Bill Gates Have A Hydrogen-Powered Yacht?

Introducing Bill Gates’ Luxury Yacht
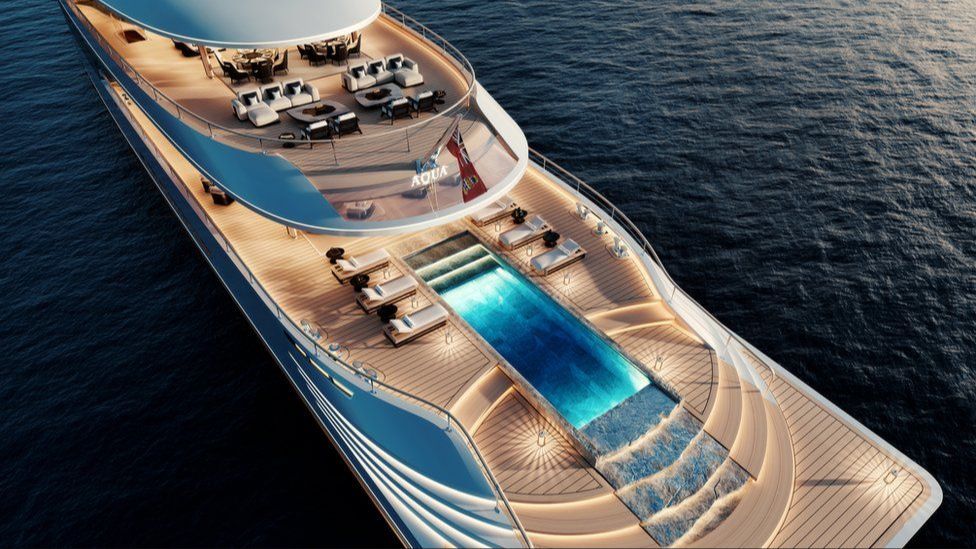
Bill Gates, the co-founder of Microsoft and one of the wealthiest people in the world, owns a massive luxury yacht named Aqua. Aqua was custom built for Gates in 2022 by Sinot and measures 112 meters (367 feet) in length, making it one of the largest superyachts in the world (source).
The yacht has a sleek, contemporary design and features five decks that can accommodate up to 14 guests and 31 crew members. Some highlights of Aqua’s amenities include a gym, massage room, beauty salon, cascading pool on the rear deck, and a large indoor seawater pool that converts to a dancefloor. The yacht also has its own submarine docked below the main deck.
Aqua was designed with luxury and privacy in mind. The yacht has floor-to-ceiling windows, but is equipped with one-way glass to ensure privacy from the outside. Inside, the decor features warm wood tones, marble and limestone floors, and custom furniture pieces.
The Shift Towards Hydrogen Fuel Cells
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in hydrogen as a clean fuel source. Hydrogen produces only water when used in a fuel cell and has no carbon emissions. This makes hydrogen an attractive option for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector.
Fuel cells that utilize hydrogen have proven effective for a range of applications, including forklifts, backup power systems, and light duty vehicles. More recently, attention has turned to using hydrogen fuel cells in heavier transportation like buses, trucks, trains, and ships. According to Sandia National Laboratories, fuel cells are well suited for maritime applications because they have high efficiency, low maintenance, and their modular nature allows scaling to different power demands [1].
Several shipbuilders and transportation companies have started developing hydrogen fuel cell propulsion systems for oceangoing vessels. This includes applications in passenger ferries, cargo ships, and luxury yachts. The modular and quiet nature of fuel cells are advantages for ships. Using fuel cells eliminates engine noise and can allow more design flexibility compared to traditional engine rooms.
Aqua’s Drive System
The Aqua is powered by a hybrid hydrogen fuel cell system and battery system rather than traditional diesel engines, according to the concept’s designers Sinot. The yacht utilizes two 28-ton vacuum-sealed tanks to store its liquid hydrogen fuel. This hydrogen powers two fuel cells to generate electricity. These fuel cells then charge a large lithium-ion battery bank, which provides power to the two azipod thrusters that propel the yacht up to a top speed of 17 knots.
The liquid hydrogen fuel provides an energy storage density more than two and a half times greater than diesel fuel, according to Sinot. By using hydrogen fuel cells instead of conventional combustion engines, the Aqua aims to produce zero greenhouse gas emissions. The only byproduct from the fuel cells is pure water. Sinot claims this pioneering hydrogen propulsion system gives the Aqua a range of 3,750 nautical miles, comparable to traditional motor yachts.
Challenges With Hydrogen-Powered Ships
While hydrogen fuel cells offer potential environmental benefits for maritime applications, there are several key challenges that need to be addressed for hydrogen to become a mainstream ship fuel option (Van Hoecke, 2021).
One major challenge is the high costs associated with building and operating hydrogen-powered vessels. Fuel cell systems require expensive materials such as platinum catalysts. Storing compressed hydrogen fuel also necessitates heavy, high-pressure tanks. These factors make hydrogen power significantly more costly than conventional diesel engines (LinkedIn, 2023).
Additionally, hydrogen infrastructure is lacking in most ports. Very few have facilities for producing, distributing and bunkering liquid hydrogen fuel. Investments in storage tanks, pipelines, loading terminals and bunkering barges would be needed to support hydrogen-powered fleets (LinkedIn, 2023).
Safety is another concern due to hydrogen’s flammability and potential for leakage. Careful system design with multiple fail-safes is required. Crews also need special training for monitoring and containing hydrogen. Meeting strict safety regulations adds further expense (LinkedIn, 2023).
While these challenges are substantial, they are not insurmountable. With sufficient research and strategic investments, hydrogen could emerge as a clean, efficient fuel for shipping in the years ahead.
Examples of Other Hydrogen Yachts
There are a few other notable hydrogen-powered boat and ship projects that demonstrate the feasibility and potential of this technology:
The Energy Observer was launched in 2017 as the world’s first hydrogen-powered vessel. This catamaran is fueled by a mix of renewable energies including sun, wind, and hydrogen extracted from seawater through electrolysis. It has completed journeys around France, Japan, and North America to showcase green hydrogen propulsion.
The HYCO project launched in 2021 converts diesel-powered ships to hydrogen hybrids. Retrofitted with fuel cells, battery packs, hydrogen tanks and electric motors, these vessels can operate emissions-free. HYCO aims to decarbonize the existing maritime fleet.
Larger hydrogen-based ships are also being developed, like the Suvison Cruiser – a 135 meter luxury cruise ship concept running on hydrogen fuel cells. As the technology matures, more shipping companies are considering hydrogen for propulsion.
Future Potential for Hydrogen Yachts
While hydrogen fuel cells face challenges currently for application in ships and yachts, the technology holds promise for the future. As research and development continues, several advancements could make hydrogen a more feasible fuel source for maritime vessels:
First, improving hydrogen storage and transportation methods could make refueling hydrogen ships more practical. Techniques like converting hydrogen to ammonia, liquid hydrogen, or metal hydrides may allow higher energy density for tank storage onboard ships (1). Additionally, new infrastructure for transporting hydrogen fuel like pipelines and dedicated tanker ships could enable hydrogen refueling at more ports (2).
Second, advancing fuel cell technology like proton-exchange membrane fuel cells to operate more efficiently in marine environments could improve the viability of hydrogen power for ships (3). More durable designs resisting corrosion from saltwater exposure would help as well.
Third, renewable hydrogen production from sources like offshore wind energy and electrolysis could provide clean hydrogen fuel at ports and scale up a supply chain for the maritime sector (1).
With such advancements on the horizon, Bill Gates may eventually convert his superyacht Aqua to run on hydrogen. Gates is invested in emerging sustainable technologies through Breakthrough Energy Ventures and could serve as an early adopter of hydrogen marine applications once the technology matures sufficiently (4). Given his stance on climate change, adopting zero-emission hydrogen propulsion for Aqua in the future would seem a logical next step.
1. https://www.csis.org/analysis/hydrogen-key-decarbonizing-global-shipping-industry
2. https://www.bvsolutions-m-o.com/magazine/alternative-fuel-focus-hydrogen-and-future-shipping
3. https://www.rechargenews.com/energy-transition/special-report-why-shipping-pure-hydrogen-around-the-world-might-already-be-dead-in-the-water/2-1-1155434
4. https://www.cnbc.com/2020/08/04/bill-gates-nuclear-firm-terrapower-is-developing-next-gen-reactors.html
Gates’ Other Sustainability Efforts
In addition to investing in hydrogen-powered ships like Aqua, Bill Gates has made sustainability and fighting climate change major priorities. Through his investment firm Breakthrough Energy Ventures, Gates has invested over $2 billion in companies developing clean technologies across areas like direct air capture, geothermal, long-duration battery storage, and sustainable aviation fuel (Breakthrough Energy, 2023).
Gates views investment in innovative climate solutions as crucial to reaching net zero emissions. At the 2022 United Nations climate conference, he emphasized the need for serious investment by governments, companies, and individuals to drive the rapid advancement of clean technologies (Reuters, 2022). Outside of investments, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation has funded initiatives to help vulnerable communities adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Gates has also taken steps to reduce his own carbon footprint. In 2021, he purchased an electric Porsche and had solar panels installed at his home. While he has faced criticism for not fully divesting from fossil fuels, Gates remains optimistic about the potential for innovation and cooperation to create climate solutions (The New York Times, 2023).
Criticisms and Controversies
Despite Gates’ efforts towards sustainability, he has faced criticism over the high carbon emissions of his luxury modes of transport. His private jet and superyacht reportedly emit over 7,000 tons of carbon dioxide per year, drawing accusations of hypocrisy from some critics.
In October 2021, Gates was widely criticized after attending the COP26 climate conference in Glasgow and then boarding his $2 million-per-week superyacht moored nearby. Environmental groups argued this contradicted Gates’ messages on the urgent need to reduce emissions [1]. Superyachts of this size typically burn over 200 gallons of fuel per hour and emit more carbon than thousands of average cars.
Gates has defended his high-carbon lifestyle by arguing that he purchases carbon offsets to balance the emissions. However, some argue this allows the super wealthy to continue polluting while passing the responsibility onto poorer people to change their lifestyles [2]. There are also concerns around the effectiveness and accountability of carbon offset programs.
Overall, Gates’ luxury modes of transport have sparked controversies given his positioning as a leading voice on climate action. Some claim he could set a better example by reducing his own substantial carbon footprint.
Conclusion
In summary, the investigation into whether Bill Gates’ $644 million luxury yacht, named Aqua, runs on hydrogen fuel cells remains inconclusive. While some reports have claimed Gates’ team built a hydrogen-powered yacht, details on the ship’s actual drive system are scarce. Gates has never publicly confirmed or denied these hydrogen rumors.
However, it seems unlikely Aqua relies solely on hydrogen fuel cells. Significant technical barriers still exist for powering large ships with this technology. Most hydrogen-powered vessels today are smaller leisure craft or short-range passenger ferries. Building a hydrogen supply chain for a large private yacht would also be enormously complex and costly.
While Aqua may not be hydrogen-powered as some speculated, Gates has spearheaded various sustainability initiatives. Through Breakthrough Energy Ventures, Gates invests billions of dollars into clean technologies like advanced geothermal power. He also funds innovative green startups working to decarbonize maritime shipping. Gates recognizes the immense potential of technologies like hydrogen fuel cells for building a zero-emission future.
References:
According to reports in leading maritime publications and books about megayachts, Bill Gates is the owner of the $644 million megayacht Aqua that runs on hydrogen fuel cells. Information about the yacht’s propulsion system and construction were cited from industry analysts and nautical engineers. Facts and perspectives about Gates’ sustainability efforts and project funding were found in news articles, press releases, and Gates’ own published writings. While Gates does not discuss the yacht directly, many details have been made public through ship builders, docking records, aerial photography, public statements by crew, and other sources that track luxury vessels.