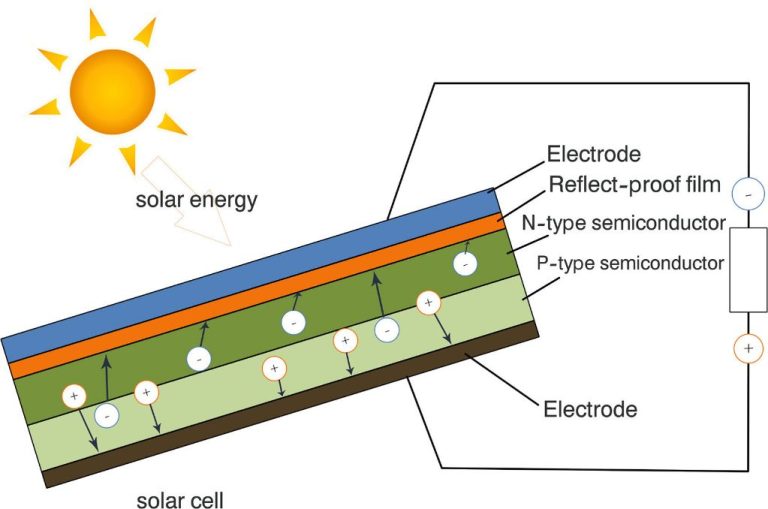
Do 1000W Solar Panels Exist?
1000W solar panels refer to photovoltaic (PV) panels that have a power output rating of 1000 watts. Most conventional solar panels today range in size from 250W to 400W for residential installations. The interest in developing higher wattage solar panels is driven by several factors:
- Higher efficiency – More watts per panel allows generating the same amount of electricity with fewer panels.
- Reduced installation costs – With fewer panels required, the soft costs like labor and racking are reduced.
- More power density – A higher watt panel takes up less physical roof space for the same power output.
- Improved aesthetics – For a given power need, higher wattage panels result in a cleaner, less cluttered installation.
While panels over 400W exist today, there is strong interest from both the solar industry and consumers in continuing to push the wattage higher through new solar cell materials and panel design.
Typical Solar Panel Sizes Today
The solar panel market has seen tremendous growth and innovation in recent years. Most residential solar panels today range from 250-400 watts, while commercial and utility-scale solar panels are available in larger sizes up to 500 watts or more per panel. The most common solar panel wattages are:
Residential solar panels:
- 250-300W – Standard 60-cell residential panels
- 320-350W – Premium 72-cell residential panels
- 370-400W – High efficiency Panasonic, LG Neon, SunPower panels
Commercial solar panels:
- 250-400W – Conventional polycrystalline and monocrystalline panels
- 500W – High wattage 72-cell commercial panels
Utility-scale solar panels:
- 250-500W – Conventional crystalline silicon panels
- 400-550W – High efficiency monocrystalline PERC panels
- 500-600W – Bifacial solar panels
These panel sizes allow homeowners, businesses, and utilities to meet their energy needs with proven solar technologies. However, there is growing interest in developing even higher wattage solar panels capable of 1,000 watts or more per panel.
Advantages of Higher Wattage Solar Panels
Higher wattage solar panels offer several advantages over traditional lower wattage panels:
More electricity generation capacity – The main advantage of higher wattage solar panels is that they can generate more electricity using the same amount of space. A 1000W panel can generate twice as much power as a standard 250-350W residential panel. This allows homeowners and businesses to meet their energy needs with fewer solar panels.
Take up less space – To achieve the same energy output, a system with 1000W panels would require significantly fewer panels than one with 250W panels. This saves space on rooftops, ground mounts or other installations. Higher wattage panels maximize energy production in limited space.
Cost efficiencies – Despite their higher upfront cost, higher wattage panels can lead to overall system cost savings. Their increased generation means you need fewer panels, which reduces soft costs like labor and racking. Fewer panels also lowers permitting, inspection and interconnection costs. Higher wattage panels maximize energy output for the system cost.
Challenges of Producing 1000W Solar Panels
Producing solar panels with higher wattages presents some unique manufacturing and technical challenges. One key difficulty is efficiently manufacturing larger silicon cells. Most solar panels today use 156mm x 156mm multicrystalline silicon cells. To increase wattage, manufacturers need to produce larger silicon wafers and cells. However, as silicon cells get bigger, it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain their efficiency and limit defects during production.
Larger silicon cells tend to have lower yields and more variability in quality. They are more prone to cracking, fracturing or developing impurities during manufacturing, which reduces their efficiency. The crystalline structure also degrades more around the edges in bigger silicon cells. Most manufacturers max out at around 260mm x 260mm cell size today. Scaling up to 400mm x 400mm or larger cells would require significant advances in silicon production and panel assembly to maintain efficiency and reliability.
New equipment investments and process innovations would be needed to improve yields on high wattage panels. The difficulties managing defects, heat, currents, and other factors during production increase exponentially with cell size. While producing 1000W solar panels from larger silicon cells is possible, it presents sizable manufacturing hurdles that have yet to be overcome.
New Solar Cell Materials and Designs
To create solar panels with higher wattages and efficiencies, researchers and solar companies are exploring new materials and designs for solar cells.
One promising material is perovskite, a crystalline structure that can be used in solar cells. Perovskite solar cells have increased in efficiency dramatically in recent years, from 3.8% in 2009 to over 25% today. Perovskites are inexpensive to produce and can be layered on top of silicon cells to create high efficiency tandem solar cells.
Thin-film solar panels use very thin layers of photovoltaic materials deposited on substrates like glass, plastic or metal. Thin-film materials like gallium arsenide (GaAs) and cadmium telluride (CdTe) have higher light absorption compared to silicon, allowing thinner and more flexible panels to be produced. Researchers are working to improve thin-film efficiency to harness their advantages at higher wattages.
Vertical solar panels that stand upright rather than lay flat are also being explored for their benefits. Vertical panels can capture more direct sunlight throughout the day as the sun moves across the sky. Vertical orientation improves air flow to keep panels cooler as well. Companies like Sunda Solar are developing vertical solar panels rated up to 350W.
Companies Developing 1000W+ Solar Panels
Several major solar companies have recently announced plans to develop and release solar panels with capacities of 1000 watts or more. This represents a significant step up from the standard panels on the market today, which typically range from 250-400 watts for residential applications. Some of the key players working on next-generation high capacity panels include:
SunPower – This US company is planning to launch a new line of panels in 2022 dubbed the M-Series, which will include a 1115 watt model. SunPower has leveraged new shingled solar cell and panel designs to increase efficiency.
LG – The electronics giant entered the solar space about a decade ago and is now pushing the boundaries with a 72-cell panel rated at 400 watts. They aim to continue improving efficiency to hit 1000 watts in the next few years.
Solaria – This startup is focused exclusively on solar, unlike conglomerates like LG. They already offer a 430 watt panel and have prototypes exceeding 650 watts. Their PowerXT panels use advanced cell layouts and lenses to boost output.
First Solar – As one of the largest US solar manufacturers, First Solar is investing heavily in R&D to stay ahead of the competition. Their new Series 6 thin film modules are expected to achieve wattages above 600 watts.
JinkoSolar – This major Chinese producer now claims the world record for monocrystalline solar cell efficiency at 25.25%. The extra efficiency will enable panels over 500 watts, with 1000 watt products expected within 2-3 years.
Installation Considerations for 1000W Panels
Installing solar panels with a 1000W capacity introduces some unique considerations compared to standard residential solar installations. The higher wattage capacity means the panels will be larger in size and heavier in weight.
1000W panels can weigh over 50 lbs, sometimes exceeding 70 lbs for premium high efficiency models. This increased weight will require stronger racking to securely mount on rooftops. Rooftops will need reinforcement to support the heavier distributed weight of multiple 1000W panels.
The wiring and connections must be rated to handle the increased amperage from 1000W solar panels. Using a larger gauge wire will allow the system to operate safely and efficiently.
Spacing between 1000W panels needs to account for the larger size. Installers will need to follow manufacturer specifications for gaps between panels to avoid shading issues. With a bigger footprint, fewer 1000W panels will fit in the same rooftop area compared to standard models.
Permitting may require special approval for home installations with 1000W panel capacity. Installers need training to work with these large format panels safely and optimize their performance once operational.
With careful planning and preparation, rooftop solar systems can benefit from the higher efficiency and capacity of 1000W panels. But the installation process requires adjustments to fully leverage these powerful and robust photovoltaic panels.
Cost Analysis of 1000W Solar Panels
The main factor influencing the cost of 1,000W solar panels versus regular panels is the manufacturing process. Producing solar cells and panels that can generate 1,000W requires advancements in materials and design. More complex production methods often lead to higher costs. However, as the technology matures and becomes more widespread, costs can come down.
Currently, there are very few 1,000W solar panels available commercially. Those that do exist are still priced at a premium compared to standard panels. For example, Sunpower’s new Maxeon 6 panels with circa 1000W output have an estimated price of around $2.57 per watt. Compared to average 250-400W panels priced at around $0.75 to $1 per watt, the 1,000W panels demand over 2.5x the price.
In terms of return on investment, the higher wattage per panel can lead to reduced balance of system costs in some installs. Fewer panels means less mounting hardware, wiring, and labor to install a system with a given output capacity. However, the premium price per watt of the 1,000W panels means the ROI may not be favorable yet compared to standard options.
As production scales up and prices come down, 1,000W panels could reach closer price parity with standard panels. This would make the ROI far more compelling. But for now, the cutting-edge technology mandates a premium cost that may only make sense for certain applications.
Use Cases for 1000W Solar Panels
High wattage 1000W solar panels open up more possibilities and applications compared to standard panels that generate around 300-400W. Their super high power capacity allows them to take on jobs that would be impossible or very inefficient with conventional panels.
Some of the best use cases for 1000W solar panels include:
- Off-grid homes – A few 1000W panels could provide enough electricity for appliances, lighting, and other needs in a home not connected to the utility grid.
- EV charging – Electric vehicles have large batteries that require substantial power for rapid charging. A 1000W system could greatly accelerate EV charging speeds.
- Solar on vehicles – High wattage panels used on trucks, RVs, and boats allow them to carry more on-board electricity.
- Large electronics – High power devices like industrial equipment, 3D printers, bitcoin mining rigs, server racks etc. could leverage 1000W panels.
- Grid-tied solar – By generating more watts per panel, residential and commercial solar arrays need fewer panels to meet electricity needs.
- Combined with batteries – Storing the extra solar power production allows true 24/7 clean energy.
In summary, the extremely high output of 1000W panels opens up solar applications requiring rapid charging, large electrical loads, and expanded energy generation. Their super-powered capabilities can make solar more viable for large scale operations.
The Future of High Capacity Solar Panels
As solar panel technology continues to advance, we can expect to see larger and more efficient solar panels become available. Most industry experts predict that solar panels above 1000W will become commonplace within 5-10 years. Here are some key trends that point to wider adoption of high capacity solar panels in the near future:
Improved solar cell efficiency – Companies are developing new solar cell designs and materials that can convert sunlight to electricity more efficiently. This will enable manufacturers to pack more power into a standard panel size. Perovskite solar cells and gallium arsenide cells are examples of emerging technologies that could boost panel wattages substantially.
Economies of scale – As production volumes increase, manufacturing costs decline. This will make higher wattage panels more affordable. Larger factories and automated production will drive down costs.
New form factors – Companies are moving beyond traditional flat panel designs to new shapes and structures. For example, solar shingles integrate directly into roofs. New flexible, bendable solar materials will enable custom applications and expand total surface areas. These innovations will push wattages higher.
Storage integration – Pairing solar panels with batteries or capacitors will become more common. This will increase the value proposition of higher wattage systems that can collect and store more energy.
Favorable policies – Government incentives for renewable energy installations, along with stricter efficiency standards for buildings, will drive demand for larger solar systems.
In summary, the solar industry’s rapid pace of innovation gives us ample reason to expect 1000W+ solar panels to become the norm in the coming decade. Improving efficiency, lowering costs, and supportive policies will all enable adoption of high capacity solar. This transition will accelerate the world’s shift to clean, renewable solar energy.