Did Tesla Want Electricity To Be Free?
Introducing Nikola Tesla
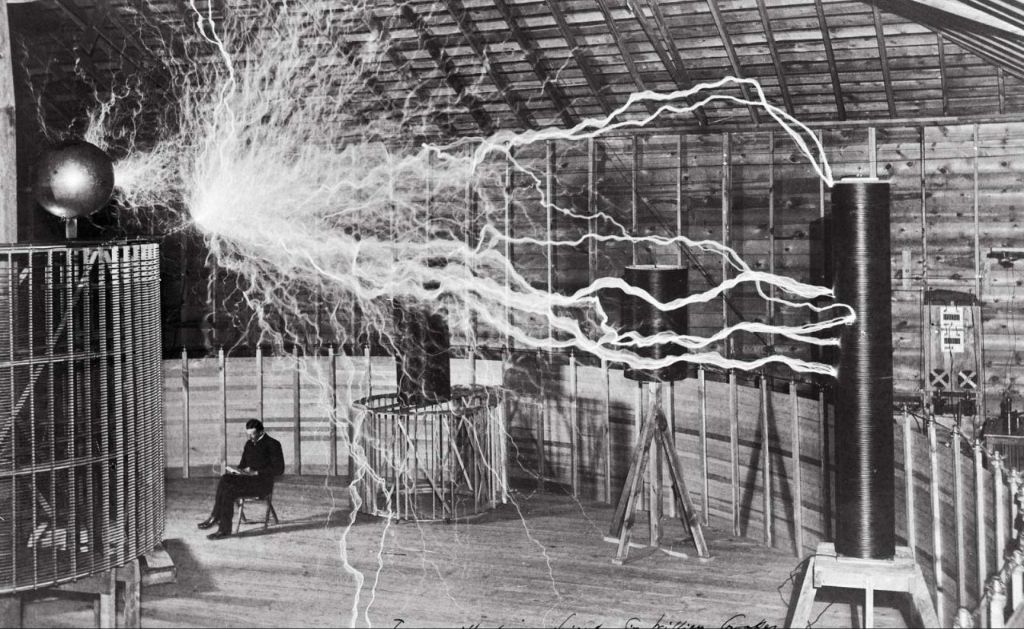

Nikola Tesla was a prolific Serbian-American inventor and electrical engineer who made breakthrough discoveries in the production, transmission, and application of electric power. He immigrated to the United States in 1884 and worked for a short time with Thomas Edison before starting his own laboratories and companies to develop a range of electrical and mechanical devices.
Some of Tesla’s most famous inventions include the Tesla coil, a high-voltage transformer circuit used to produce high-frequency alternating current electricity; the alternating current (AC) induction motor and polyphase AC system for distributing electricity; the Tesla turbine, a bladeless centrifugal flow turbine; and early contributions to radio technology.
According to Nikola Tesla Inventions from the Tesla Science Center, Tesla had over 300 different patents for his inventions and held over 700 inventions in his personal notebooks that were never patented. His inventions established the basis for modern electrical and power distribution systems that we still use today.
While Tesla had many forward-thinking ideas like wireless transmission of electricity, some of his proposed inventions like the Wardenclyffe Tower for global wireless communication were not feasible with the technology available during his lifetime. Nonetheless, Tesla’s inventions demonstrated his genius and changed the landscape of electrical engineering.
Tesla’s Vision for Electricity
Nikola Tesla had a vision of providing electricity wirelessly and for free to everyone across the world. He believed that electricity was the energy that could elevate mankind and should be available freely. In 1900, Tesla said at the American Institute of Electrical Engineers that “it is impossible to transmit electrical energy economically if we are compelled to use such means and appliances as are in use at present.” Nikola Tesla Quotes About Energy He worked for years on this vision, conducting research into wireless transmission of power and building prototypes like Wardenclyffe Tower.
Tesla dreamed of a world where electricity could be transmitted wirelessly like signals through the air, waves in the ether, so that anyone could tap into the energy freely. This was the motivation behind inventions like his Tesla Coil and Magnifying Transmitter. While initially backed financially for these wireless transmission projects, Tesla ultimately lacked the long-term funding and support needed to fully realize his vision before his death.
Wardenclyffe Tower
Nikola Tesla envisioned a global wireless transmission system and began construction of Wardenclyffe Tower in 1901 near New York to achieve this goal. The Wardenclyffe Tower in Shoreham, New York was constructed between 1901 and 1917 to be the prototype for Tesla’s “World Wireless” system that could broadcast and transmit information and electricity globally without wires.
The main purpose of the 187-foot tower was to transmit electricity wirelessly across long distances by “charging” the ionosphere. Tesla believed a correctly designed tower system would allow for virtually unlimited amounts of power to be transmitted and received wirelessly.
According to the Tesla Science Center (https://teslasciencecenter.org/history/tower/), the tower was designed to be able to broadcast and transmit information and “secure military communications” around the world. It could also broadcast news reports, transmit facsimile images and even music. Ultimately, Tesla hoped it would provide free electricity worldwide.
Tesla vs Edison
Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla were two pioneering inventors who competed to develop and commercialize electricity in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Edison developed direct current (DC) electrical systems and wanted to turn electricity into a profitable business. Tesla, on the other hand, invented alternating current (AC) systems and envisioned electricity as a service for humanity, not for commercial gain.
Tesla started working for Edison in 1884 but soon left his company due to a dispute over pay. Tesla knew that AC systems could transmit electricity over longer distances than DC. He partnered with George Westinghouse to commercialize AC while Edison stuck with DC. This set up the “War of the Currents” with Edison and Westinghouse battling to establish their electrical system as the industry standard (1).
While Edison used fear-based marketing about the dangers of AC, Tesla focused on the benefits of AC for transmitting power efficiently. The decisive victory for AC came when Westinghouse won the contract to light the 1893 Chicago World’s Fair. AC went on to become the dominant standard as it could send electricity farther using thinner wires (2).
Ultimately, Edison viewed electricity as a commodity to profit from, while Tesla cared more about harnessing electricity to benefit humanity. Tesla did not patent many of his inventions because he wanted the technology to be freely available. Edison commercialized the incandescent light bulb and power systems to make money. This contrast symbolized their different mindsets toward electricity and innovation.
Financial Backers
Tesla needed substantial financial backing to fund his ambitious electricity projects. His ideas often required large-scale facilities and equipment.
While working for Thomas Edison, Tesla secured some initial funding from the industrialists George Westinghouse and JP Morgan. Westinghouse provided capital for Tesla to develop alternating current motors and transformers while Morgan helped finance the construction of the Wardenclyffe Tower (cite url location 1). However, after the initial investments, Tesla struggled to secure ongoing support as his ideas grew increasingly experimental and expensive.
More recently, Elon Musk has been Tesla’s most significant investor and backer. Through his leadership of Tesla Motors and investments in solar energy, Musk has helped advance and commercialize some of Tesla’s visionary ideas around electricity and energy (cite url location 2). However, even with wealthy benefactors, realizing Tesla’s vision of free electricity for all has proved complicated in practice.
The Reality of Free Electricity
Nikola Tesla’s vision for providing free electricity worldwide faced substantial challenges. While his ideas like wireless power transmission were ahead of their time, the infrastructure required did not exist.
Providing electricity at no cost requires enormous capital investment in power generation and transmission equipment. Significant resources would be needed to build and maintain this infrastructure. Though Tesla secured backing for projects like Wardenclyffe Tower, he struggled to find continued funding to fully realize his vision.
According to one analysis, the economic model behind free electricity was unclear. Existing power utilities were structured as regulated monopolies that could charge rates to cover costs and profit. Without a viable business model, companies would be reluctant to take on the massive investment needed.
There were also technological limitations to transmitting electricity wirelessly in Tesla’s day. While he made progress with short distance wireless power, efficiently transmitting electricity worldwide would have required overcoming significant hurdles. Though visionary, Tesla’s ideas faced prag
Tesla’s Later Years
After the failure of Wardenclyffe, Tesla struggled to find new investors and his reputation suffered. According to Wikipedia, “Having spent most of his money, Tesla lived in a series of New York hotels, leaving behind unpaid bills.”
Tesla spent time patenting new inventions like the bladeless turbine and experimenting with the wireless transmission of energy. However, he never again achieved the prominence of his early career. Much of his later work was viewed as unrealistic by the scientific establishment.
According to the Smithsonian, “By the 1930s, Tesla had developed several inventions that were meant to innovate within the realms of robotics, remote control and computer science. Unfortunately, limited finances and other obscurities left many of these inventions unfinished.”
As an older man, Tesla lived alone in New York City, occasionally making headlines with sensational claims or provocative statements. Tesla died poor and in debt in 1943 at the age of 86.
Tesla’s Legacy
Nikola Tesla’s legacy extends far beyond the technical details of his inventions and discoveries. At his core, Tesla wanted to provide free power for the world by developing efficient and affordable electricity generation and transmission systems powered by his polyphase alternating current (AC) motor and generator designs (1). Though not all of his visions came to fruition during his lifetime, Tesla was a true pioneer who transformed how electricity is generated, transmitted, and used around the globe.
Some of the major impacts and achievements of Tesla’s work include (2):
- Developing the first practical AC motors and power transmission systems still used today
- Contributing to modern wireless technology through his experiments with electromagnetic waves and radio transmissions
- Designing efficient electrical generators, transformers, and motors to enable more widespread use of electricity
- Promoting the use of renewable hydroelectric power generation
- Conducting innovative research into X-rays, remote control vehicles, and bladeless turbine systems
- Over 300 patents granted worldwide for his inventions
While Tesla did not achieve free worldwide electricity in his lifetime, he inspired generations of engineers and inventors with his visionary thinking and breakthrough discoveries in electromagnetism and energy (3). His legacy lives on through the many technologies and conveniences of modern life that trace their origins to Tesla’s mind.
(1) https://medium.com/@CharleTheScientist/the-life-and-legacy-of-nikola-tesla-a-pioneer-of-modern-technology-3bc704d11ac5
(2) https://www.engineeringdaily.net/the-legacy-of-nikola-tesla/
(3) https://www.history.com/topics/inventions/nikola-tesla
The Future of Electricity
The idea of free, wireless electricity has captivated imaginations for over a century. Nikola Tesla himself envisioned a world where electricity could be transmitted through the air “as easily as light and with little loss of energy.” However, the reality of implementing widespread wireless power transmission on a global scale faces substantial technical and economic obstacles.
That said, advances in renewable energy technologies and smart grids are leading some experts to predict that the cost of electricity will dramatically decline in the coming decades. A UN official has suggested that by 2050, utilities may no longer need to charge for electricity at all (By 2050, Utilities Will No Longer Charge For Electricity). https://www.forbes.com/sites/jeffmcmahon/2016/01/03/by-2050-utilities-will-no-longer-charge-for-electricity-un-official/
Studies examining pathways to 100% clean electricity by 2035 also predict falling costs as renewable penetration increases (100% Clean Electricity by 2035 Study). Technology improvements and grid integration will be key to enabling very high renewable energy penetration while maintaining reliability. However, experts stress that policy and regulatory changes will be required as well.
In summary, while truly wireless power transmission still faces major obstacles, the cost of electricity from renewable sources is expected to dramatically decline in the coming decades. But regulatory changes will likely be required before electricity can become as freely available as other ubiquitous resources like air and light.
Conclusion
In summary, Nikola Tesla’s vision was to provide free, wireless electricity to everyone on earth by harnessing the planet’s natural electrical charge. Though brilliant, Tesla’s ideas were very ahead of their time and faced many challenges. The feasibility of free, unlimited electricity for all is still debatable today. Despite never fully realizing his grand vision, Tesla’s pioneering work with electricity and electromagnetism laid the foundations for much of modern technology we take for granted today. While free electricity remains elusive, Tesla’s legacy lives on through AC power, wireless transmission, electric motors, and more innovations that have undoubtedly changed the world.
Though we are not yet able to access limitless energy as Tesla dreamed, his vision remains inspirational. As technology continues to advance, perhaps we will someday achieve his goal of providing clean, abundant energy globally, for the benefit of all humanity.