Can Ribose Cause Anxiety?
What is Ribose?
Ribose is a simple sugar used by the body to produce energy. It occurs naturally in foods like RNA (ribonucleic acid), ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and nucleic acids. According to the Merriam-Webster dictionary, ribose is “a pentose C5H10O5 found especially in the dextrorotatory form as a component of many nucleosides (such as adenosine and guanosine)”.
Structurally, ribose is a 5-carbon sugar with the molecular formula C5H10O5. It contains an aldehyde functional group and is classified as an aldopentose. Ribose plays a key role in many important biological processes as it alternates with phosphate groups to form the backbone of RNA polymers. It also binds to nitrogenous bases like adenine and guanine to produce nucleosides used for energy metabolism.
Overall, ribose is an essential simple sugar that provides the foundation for RNA, ATP, and other vital cell components involved in energy production.
Ribose Supplements
Ribose supplements like D-ribose are often used by people looking to boost their energy levels. Ribose is a sugar that is used by cells to produce energy. Taking ribose supplements can increase the available ribose in the body and enhance energy metabolism (1).
Some studies have found that ribose supplements can improve symptoms in people with conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia that are characterized by reduced energy levels. For example, one study gave 41 patients with chronic fatigue syndrome either ribose or a placebo for 3 weeks. The ribose group experienced significantly greater improvements in energy levels, sleep, mental clarity, pain intensity and well-being (2).
Other research shows that ribose supplements may also increase exercise tolerance in people with conditions like heart disease. This is because ribose helps restore ATP levels in muscles, which can become depleted during exercise (3).
The typical dosage of ribose supplements ranges from 5-15 grams per day, divided into several smaller doses. It may take several weeks for the effects to be felt (4).
Sources:
(1) https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-827/ribose
(2) https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/d-ribose#_noHeaderPrefixedContent
(3) https://www.webmd.com/vitamins-and-supplements/ribose-uses-and-risks
(4) https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-827/ribose
Anxiety Overview
Anxiety is a mental health disorder characterized by excessive and persistent worry that is difficult to control. It can cause nervousness, restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension and sleep problems (1).
According to the American Psychological Association (APA), anxiety is an emotion characterized by feelings of tension, worried thoughts and physical changes like increased blood pressure. It is not the same as fear, which is an appropriate emotional response to a real threat or danger (2).
There are several types of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, panic disorder and phobias. While anxiety is a normal human response, anxiety disorders cause excessive amounts of anxiety, stress and fear that can interfere with daily life (1).
Symptoms of anxiety include feeling agitated, sweating, trembling, feelings of danger, rapid heartbeat, restlessness, sleeping difficulties and avoidance of anxiety-provoking situations (2).
Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions. However, various treatments are available, including therapy, medication and lifestyle changes (1).
Sources:
(1) https://medlineplus.gov/anxiety.html
(2) https://www.apa.org/topics/anxiety
Can Ribose Cause Anxiety?
There are some theories about a possible link between ribose supplements and anxiety. Ribose is a simple sugar that provides energy for cells in the body. It is also a component of genetic material like RNA and ATP. Some research has looked into whether high doses of ribose could have effects on the brain and behavior.
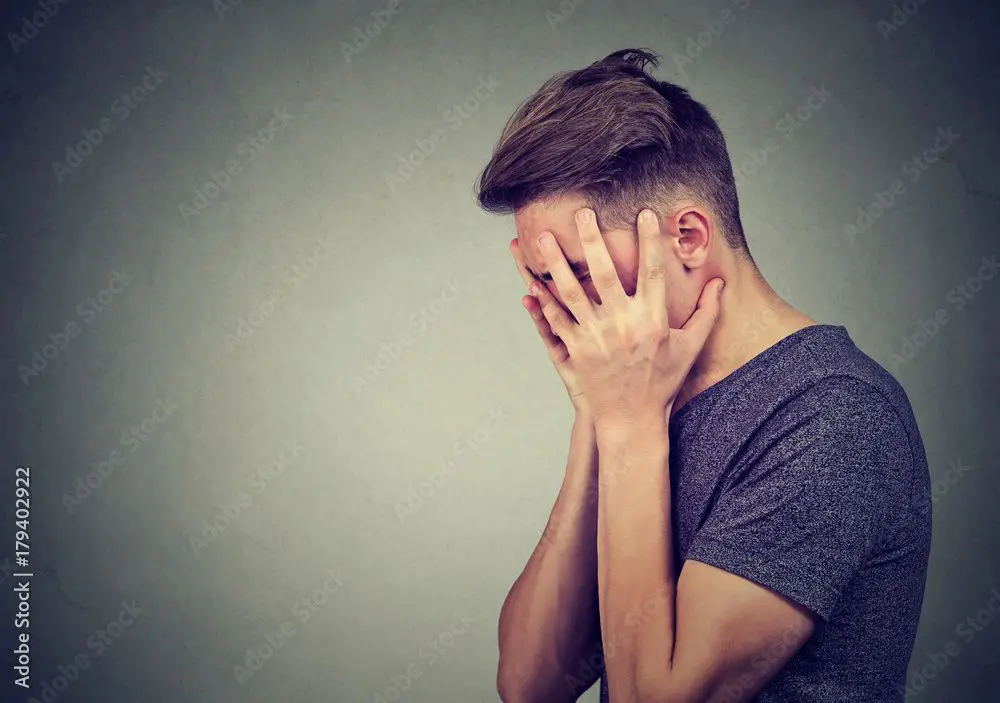

One study found that prolonged high-dose ribose administration in mice led to anxiety-like behaviors as well as cognitive impairment [1]. The researchers theorized that excess ribose could interfere with purine metabolism in the brain. This might lead to altered levels of purine metabolites that play roles in neurotransmission. Disturbances in brain chemistry could potentially contribute to anxiety symptoms.
Another study in mice also found an association between chronic high-dose ribose intake and depressive- and anxiety-like behaviors [2]. The researchers suggested oxidative stress resulting from ribose metabolism may impact emotional regulation in the brain.
However, the ribose dosages used in these animal studies were quite high. So far, there is limited research on whether supplemental doses in humans could also affect anxiety levels.
Mechanisms
There are a few possible mechanisms that may link ribose supplementation to increased anxiety:
One study found that giving mice high doses of D-ribose led to the accumulation of amyloid beta and hyperphosphorylated tau proteins in the brain, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease and anxiety (1). The buildup of these proteins may contribute to neurodegeneration and psychiatric symptoms.
Additionally, chronic ribose overload appears to cause oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, according to animal studies (2). Oxidative stress can lead to neuron damage and has been linked to anxiety disorders.
High doses of ribose may also impair spatial memory and learning (3). Memory deficits are commonly associated with anxiety. More research is needed to fully understand the effects of ribose on the brain and mental health.
Research Findings
Several studies have examined whether there is a connection between ribose supplements and anxiety.
A 2015 study published in PLOS One found that giving mice high doses of D-ribose led to anxiety-like behaviors. The researchers gave the mice D-ribose through a feeding tube over the course of 7 days. By the end of the study, the mice showed multiple signs of anxiety including decreased movement in open spaces, increased freezing behavior, and avoidance of bright lights [1].
Another study published in Translational Psychiatry in 2021 looked at the effects of chronic D-ribose and D-mannose overload in mice. The researchers found that overloading mice with either ribose or mannose for 8 weeks resulted in anxiety-like behaviors. The study provided evidence that high sugar intake can negatively impact mental health [2].
Overall, the available research indicates that extremely high doses of ribose may contribute to anxiety-like symptoms in animal models. However, more studies are needed to determine if ribose supplements cause anxiety in humans at normal supplemental doses.
Anecdotal Reports
There are several personal accounts online of people experiencing increased anxiety after taking ribose supplements. On forums and in reviews, some users have reported feeling more anxious, nervous, jittery, and on edge after starting ribose.
For example, one Reddit user said that after taking ribose, “my generalized anxiety went through the roof almost immediately” and it gave them “the jitters” even though they had no prior issues with anxiety (1). Another user on a forum also noticed ribose caused “nervous energy and some anxiety” for them (2).
Some reasons put forth for why ribose may cause anxiety for certain individuals include potentially altering levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate that regulate mood (3, 4). Those prone to anxiety seem to be more affected. However, these accounts remain anecdotal and more research is still needed on ribose’s effects on anxiety and nervous system function.
Sources:
(1) https://www.reddit.com/r/Nootropics/comments/7zs9q4/dribose_gave_me_the_jitters/
(2) https://forums.phoenixrising.me/threads/d-ribose-experiences.11482/page-2
(3) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4741441/
(4) https://www.nature.com/articles/s41398-020-01126-4
Other Factors
Anxiety disorders can have many causes unrelated to ribose or any other dietary supplements. Anxiety may arise from an underlying mental health condition, stressful life events, medical problems, or a combination of these factors.
Common mental health conditions associated with anxiety include generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, phobias, social anxiety disorder, OCD, and PTSD. These disorders, as well as others, are recognized psychiatric conditions with complex causes that require diagnosis and treatment from a mental health professional.
Major life stressors may also trigger anxiety, especially for those with a predisposing vulnerability. Examples of stressful events that can cause anxiety include traumatic experiences, relationship difficulties, financial troubles, chronic illnesses, academic pressures, and many others. Anxiety arising from life stressors may improve once the individual adapts to the situation or the stressor resolves.
Underlying medical conditions can also lead to anxiety symptoms due to the physiological effects of disease. Conditions that are known to potentially cause anxiety include hyperthyroidism, hypoglycemia, asthma, COPD, heart disease, and irritable bowel syndrome, among others. Consulting a doctor to evaluate and manage any medical conditions can help alleviate associated anxiety.
In summary, while ribose supplements may raise questions about anxiety risk in some individuals, anxiety disorders often stem from psychological vulnerabilities, major life stress, and medical problems unrelated to dietary supplements. Since anxiety has many potential causes, making lifestyle changes, seeking counseling, and getting medical attention may help address anxiety symptoms more effectively than focusing solely on ribose intake.
Precautions
While more research is still needed, some precautions can be taken for those concerned about potential links between ribose supplements and anxiety:
Start with a low dose and increase slowly. Taking too much ribose at once may contribute to side effects like anxiety. Begin with just 1-2 grams per day and gradually build up over several weeks if desired (D-Ribose: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, Dosage).
Take occasional breaks from ribose. Cycling on and off ribose supplements may help reduce any potential side effects. Try taking it daily for 3-4 weeks, then taking a 1 week break.
Watch for symptoms. Pay attention to any emerging feelings of nervousness, restlessness, tension, or panic and discontinue use if they occur. Symptoms related to anxiety may be a sign to stop ribose (Gavage of D-Ribose induces Aβ-like deposits, Tau …).
Consult a doctor. Discuss ribose supplements with your physician, especially if you have a history of anxiety disorders. They can help determine if ribose is appropriate for you.
Avoid long-term use. Due to limited safety data, it may be best to limit ribose supplementation to 8-12 weeks at a time (RIBOSE – Uses, Side Effects, and More).
Summary
Based on the research analyzed, the evidence linking ribose supplementation to anxiety is inconclusive. Some studies in mice have found that high doses of ribose can cause anxious behaviors and impair cognitive function [1]. However, human studies are limited. Anecdotal reports from ribose users are mixed, with some people reporting increased anxiety and others not noticing any effect.
Overall, more research is needed to determine if ribose can directly cause anxiety in humans at normal supplemental doses. Individuals already prone to anxiety or panic attacks should exercise caution with ribose and be aware of potential effects. Start with low doses and monitor symptoms. Anyone experiencing increased anxiety after taking ribose may want to stop usage. As with any supplement, consult your doctor before starting ribose, especially if you have a history of anxiety disorders.